文章目录
前序/先序/根遍历
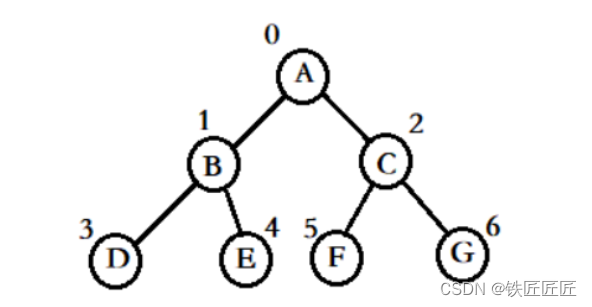
我们拿上图来举例
前序/先序/根遍历:
根遍历的原理就是,先遍历根,然后再遍历左子树,然后右子树
一句话来讲,就是 中 -> 左 -> 右
所以我们按如上顺序来算的话
先遍历根树 A 之后根结束,开始遍历左子树
于是到子树 B 发现B子树是D和E的"根"节点,于是继续向下寻找
继续到子树 D 之后就没有其他子树了,于是开始遍历右子树
继续到子树 E 之后就没有其他子树了,因为已经全部遍历完了,开始回溯到B,再回溯到A,之后在开始遍历右子树
继续到子树 C 发现C子树是F和G的"根"节点,于是继续向下寻找
继续到子树 F 之后就没有其他子树了,于是开始遍历右子树
继续到子树 G 之后就没有其他子树了,因为已经全部遍历完了,开始回溯到B,再回溯到A,结束遍历
所以根遍历的顺序就是
A->B->D->E->C->F->G

递归的方式:
c
void preOrder(TreeNode* T)
{
if(T == NULL)
return;
else
{
printf("%c->",T->data);
preOrder(T->lchild);
preOrder(T->rchild);
}
}非递归的方式,思想类似与栈的方式

验证代码
c
/*可以输入
ABD##E##CF##G##
来进行验证
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define size 20
typedef struct TreeNode
{
char data;
struct TreeNode *lchild;
struct TreeNode *rchild;
}TreeNode;
typedef struct Node
{
TreeNode *data;
struct Node *next;
}Node;
void createTree(TreeNode** T,char* temp,int* index)
{
char ch;
ch = temp[*index];
(*index)++;
if( ch == '#') *T = NULL;
else
{
*T =(TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
(*T)->data = ch;
createTree(&(*T)->lchild,temp,index);
createTree(&(*T)->rchild,temp,index);
}
}
// 前序/先序/根遍历
void preOrder(TreeNode* T)
{
if(T==NULL)
return;
else
{
printf("%c->",T->data);
preOrder(T->lchild);
preOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
Node* initQueue()
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = NULL;
node->next =NULL;
return node;
}
void enQueue(TreeNode* data, Node* list)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
node->data = data;
while(list->next)list=list->next;
node->next = list->next;
list->next=node;
}
int isEmpty(Node* Q)
{
if(Q->next == NULL)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
Node* deQueue(Node* Q)
{
if (isEmpty(Q))
return NULL;
else
{
Node *node = Q->next;
Q ->next = node->next;
return node;
}
}
void levelTraverse(Node* Q, TreeNode* T)
{
enQueue(T, Q);
while (!isEmpty(Q))
{
Node* node = deQueue(Q);
printf("%c->", node->data->data);
if (node->data->lchild)
{
enQueue(node->data->lchild, Q);
}
if (node->data->rchild)
{
enQueue(node->data->rchild, Q);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
TreeNode *T;
int i=0;
char *temp=NULL;
Node* Q = initQueue();
temp=(char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (size+1));
gets(temp);
createTree(&T,temp,&i);
preOrder(T);
printf("\n");
levelTraverse(Q, T);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}往期回顾
1.【第一章】《线性表与顺序表》
2.【第一章】《单链表》
3.【第一章】《单链表的介绍》
4.【第一章】《单链表的基本操作》
5.【第一章】《单链表循环》
6.【第一章】《双链表》
7.【第一章】《双链表循环》
8.【第二章】《栈》
9.【第二章】《队》
10.【第二章】《字符串暴力匹配》
11.【第二章】《字符串kmp匹配》
12.【第三章】《树的基础概念》
13.【第三章】《二叉树的存储结构》
14.【第三章】《二叉树链式结构及实现1》