文章目录
前言
本文建立在前两篇文章的基础上学习
树、二叉树
二叉树的遍历与操作
请大家多多支持
二叉树面试热门题目
注:该部分出现的所有题目都可以在力扣上面找到原题,大家可以去官网尝试自己做一下,题目与我写的注释题目基本一样。
java
//翻转二叉树
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
if(root.right == null && root.left == null){
return root;
}
TreeNode tmp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = tmp;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}翻转二叉树借用tmp作为中间变量交换左右子树的值。
java
//检查两棵树是否相同
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
if(p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null){
return false;
}
if(p.val == q.val){
boolean leftRet = isSameTree(p.left,q.left);
if(!leftRet){
return false;
}
boolean rightRet = isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
if(!rightRet){
return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}先判断结构是否一样,再判断具体的值是不是一样。
java
//对称二叉树
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
if(p == null && q != null || p != null && q == null){
return false;
}
if(p.val == q.val){
boolean leftRet = isSymmetricChild(p.left,q.right);
if(!leftRet){
return false;
}
boolean rightRet = isSymmetricChild(p.right,q.left);
if(!rightRet){
return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}除了根节点之外,把树分成左右两部分,其实就成了判断是不是树相同。
java
//另一颗树的子树
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
if(root.val == subRoot.val){
if (isSameTree(root,subRoot)){
return true;
}else{
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)){
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)){
return true;
}
}
}
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)){
return true;
}
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)){
return true;
}
return false;
}本质也是比较树是否相同,但是要先找到小树根节点所对应的大树里面的结点。
java
//平衡二叉树
/*
* 时间复杂度O(n^2)
* */
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return true;
}
if(!isBalanced(root.left)){
return false;
}
if(!isBalanced(root.right)){
return false;
}
int h = getHeight(root.left) - getHeight(root.right);
if(h < -1 || h > 1){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
// 获取二叉树的高度
public int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
return Math.max(getHeight(root.left),getHeight(root.right)) + 1;
}首先平衡二叉树的概念是两边高度差不能大于1。这第一种方法做起来比较容易,但是时间消耗大。
java
//平衡二叉树
/*
* 时间复杂度O(n)
* */
public boolean isBalanced2(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return true;
}
return getHeight2(root) >=0;
}
public int getHeight2(TreeNode root){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = getHeight2(root.left);
if(left == -1){
return -1;
}
int right = getHeight2(root.right);
if(right == -1 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1){
return -1;
}else{
return Math.max(left,right) + 1;
}
}时间复杂度大的原因是getHeight最坏要遍历每个结点,现在改为下面的结点出了问题返回-1判断就行,不用一步步再重新找高度。
java
//最近的祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(root == p || root == q){
return root;
}
if(left != null && right != null){
return root;
}else if(left != null){
return left;
}else{
return right;
}
}
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> stack){
if(root == null){
return false;
}
stack.push(root);
if(root != node){
boolean ret = getPath(root.left,node,stack);
if(ret){
return true;
}
ret = getPath(root.right,node,stack);
if(ret){
return true;
}
}else{
return true;
}
stack.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor2(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
Stack<TreeNode> stackP = new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stackQ = new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,stackP);
getPath(root,q,stackQ);
int n = stackP.size() - stackQ.size();
if(n > 0){
while(n > 0){
stackP.pop();
n--;
}
}else{
n = -n;
while(n > 0){
stackQ.pop();
n--;
}
}
TreeNode ret = null;
while(!stackQ.isEmpty() && !stackP.isEmpty()){
if(stackQ.peek() == stackP.peek()){
ret = stackQ.peek();
break;
}else{
stackQ.pop();
stackP.pop();
}
}
return ret;
}最近的祖先也是两种方法,首先第一种我的建议是直接画图,当然我这张图画的比较抽象,大家可以自己尝试一下,不画图的话自己理解起来很麻烦,我当时也是看了好久才明白。
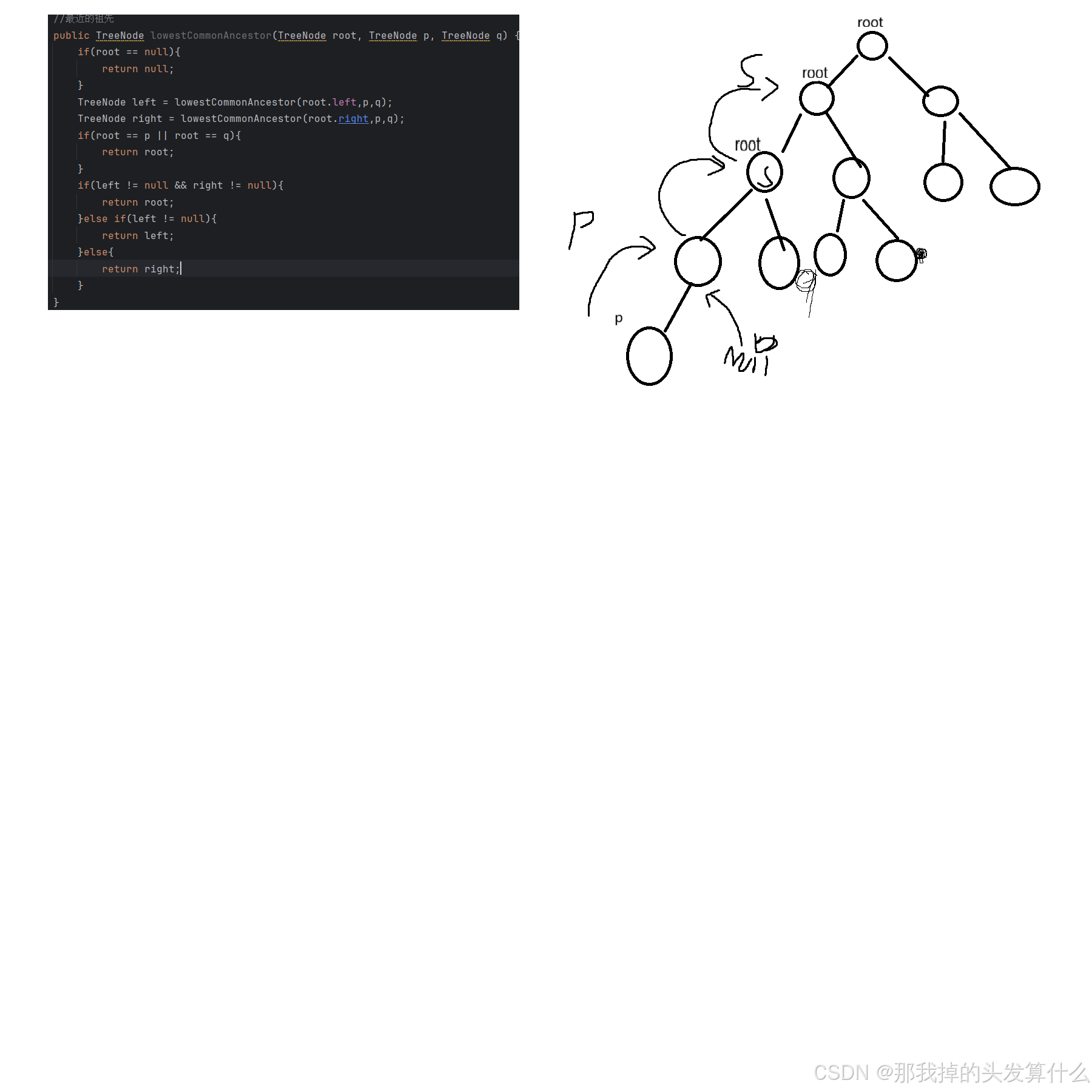
第二种方法比较巧妙,找到pq路上所有的点,再把公共祖先之前的点都出栈,最后栈顶的就是公共祖先了。
java
public class buildTreeUsedPreAndInOrder {
static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;//存储左孩子的引用
public TreeNode right;//存储右孩子的引用
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public int preIndex;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend) {
//这种情况下 表明 当前root 没有子树了
if(inbegin > inend) {
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
int rootIndex = findVal(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
preIndex++;
root.left = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,rootIndex-1);
root.right = buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,rootIndex+1,inend);
return root;
}
private int findVal(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int val) {
for(int i = inbegin ;i <= inend;i++) {
if(inorder[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}众所周知知道中序序列和其他任意一种序列就能得到唯一的二叉树,这里用前序中序构造二叉树,主要思路是,通过前序先找到根节点,然后根据根节点在中序序列中的位置确定左右子树,然后继续根据前序确定左右子树根节点以此类推。
java
public class buildTreeUsedPostAndInOrder {
static class TreeNode {
public int val;
public TreeNode left;
public TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
postIndex = postorder.length - 1;
return buildTreeChild(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length - 1);
}
public int postIndex;
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] inorder, int[] postorder, int inbegin, int inend){
if(inbegin > inend){
return null;
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);
int rootIndex = findIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,postorder[postIndex]);
postIndex--;
root.right = buildTreeChild(inorder,postorder,rootIndex + 1,inend);
root.left = buildTreeChild(inorder,postorder,inbegin,rootIndex -1);
return root;
}
private int findIndex(int[] inorder,int begin,int end,int val){
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
if(inorder[i] == val){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}这个思路就相反,后序序列要从后往前遍历确定根节点,然后重复一样的操作。
java
//根据二叉树创建字符串
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return null;
}
StringBuilder stringbuilder = new StringBuilder();
tree2strchild(root,stringbuilder);
return stringbuilder.toString();
}
public void tree2strchild(TreeNode root,StringBuilder stringbuilder){
if(root == null){
return;
}
stringbuilder.append(root.val);
if(root.left != null){
stringbuilder.append("(");
tree2strchild(root.left,stringbuilder);
stringbuilder.append(")");
}else{
if(root.right == null){
return;
}else{
stringbuilder.append("()");
}
}
if(root.right != null){
stringbuilder.append("(");
tree2strchild(root.right,stringbuilder);
stringbuilder.append(")");
}else{
return;
}
}
这道题其实不难,但是很可能不会审题,读懂题目的话就很简单。
总结
本文围绕二叉树面试高频题型展开,将二叉树的核心特性与实用算法结合,覆盖了从 "结构操作" 到 "逻辑判断"、从 "树的构造" 到 "数据转换" 的全场景问题,是对前期树结构基础与遍历逻辑的实战深化。
这些题目不仅是面试高频考点,更串联起二叉树的核心能力:递归分治、遍历应用、结构分析、效率优化。掌握它们既能夯实二叉树基础,也能为后续学习 BST、AVL 树等复杂树结构铺路,建议结合力扣原题反复练习,将 "思路" 转化为 "代码本能",真正吃透二叉树的解题逻辑。