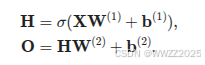目录
[1 定义](#1 定义)
[1.1 感知机](#1.1 感知机)
[1.2 多层感知机(MLP, Multi-Layer Perceptron)](#1.2 多层感知机(MLP, Multi-Layer Perceptron))
[2 常见激活函数](#2 常见激活函数)
[2.1 Sigmoid激活函数](#2.1 Sigmoid激活函数)
[2.2 Tanh激活函数](#2.2 Tanh激活函数)
[2.3 ReLU激活函数](#2.3 ReLU激活函数)
[3 多层感知机从零实现](#3 多层感知机从零实现)
[3.1 导入库及数据集](#3.1 导入库及数据集)
[3.2 初始化模型参数](#3.2 初始化模型参数)
[3.3 模型](#3.3 模型)
[3.4 损失函数](#3.4 损失函数)
[3.5 训练](#3.5 训练)
[3.6 绘制图像](#3.6 绘制图像)
[3.7 结果](#3.7 结果)
[4 多层感知机简洁实现](#4 多层感知机简洁实现)
[5 兼容性修正](#5 兼容性修正)
[5.1 安装](#5.1 安装)
[5.2 验证版本](#5.2 验证版本)
[5.3 测试代码](#5.3 测试代码)
因d2l包兼容性问题,无法调用train_ch3库,故本文中代码有所修改;如需使用train_ch3见5 兼容性修正。
1 定义
1.1 感知机
最简单的二分类问题,输入x1,x2,...,xn,输出0或1,寻找w,b,将样本分为两类。单层感知机只可产生线性分割面,无法处理XOR问题,故引出多层感知机。
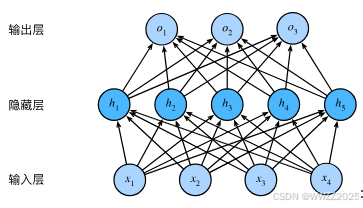
1.2 多层感知机(MLP, Multi-Layer Perceptron)
相较于感知机,多了隐藏层。需要激活函数激活,可以更近似的表示为目标非线性关系。激活函数详情如下2。
多层感知机经激活函数非线性化的公式为:
其中H为隐藏层非线性化后的输出,O为最终经非线性化后的输出。角标对应第几层。
PS.多层感知机与激活函数之间的关系
多层感知机输出是线性,经过激活函数将每一层输出非线性化后变为更加近似的目标函数
2 常见激活函数
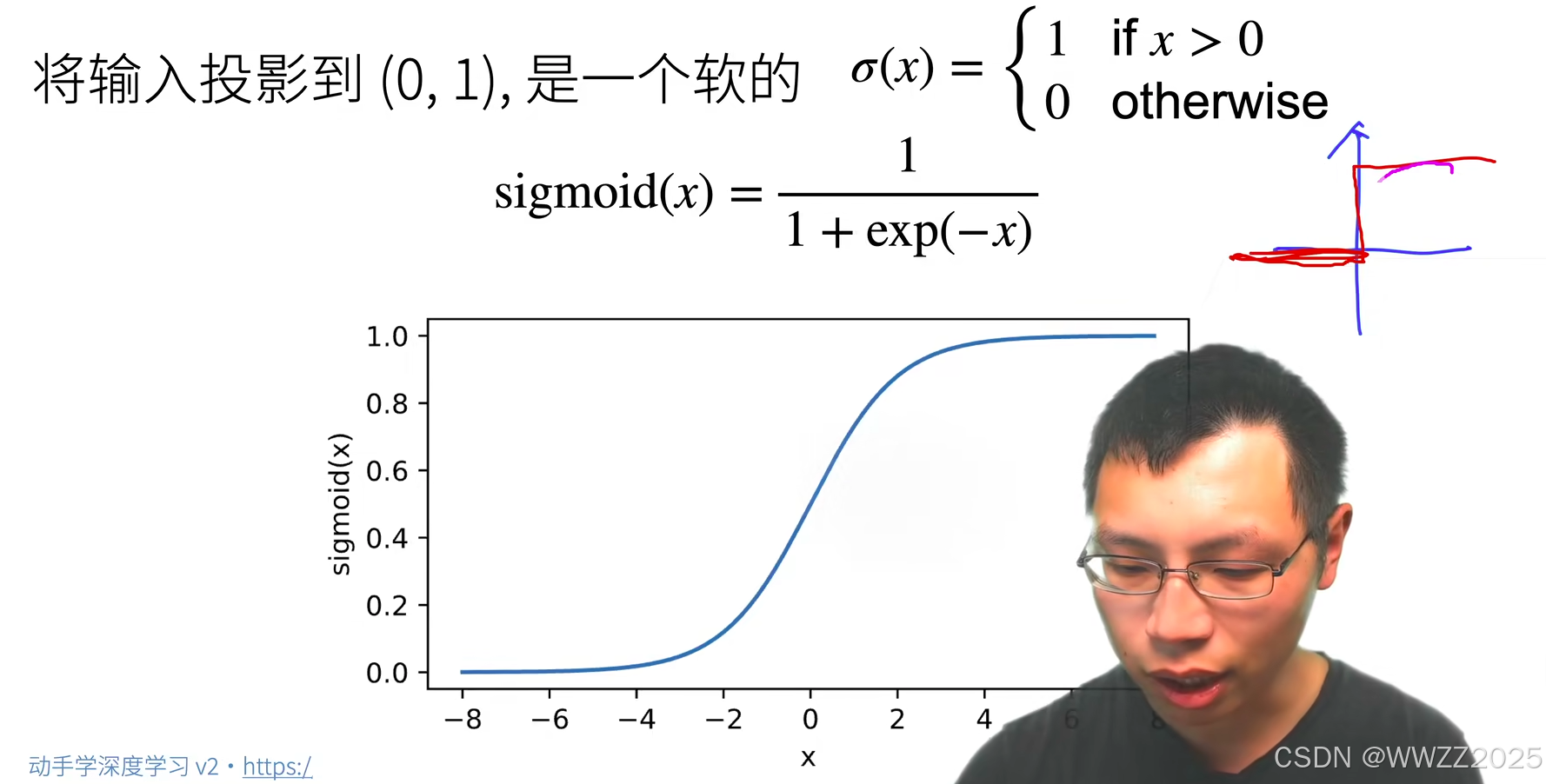
2.1 Sigmoid激活函数
2.2 Tanh激活函数
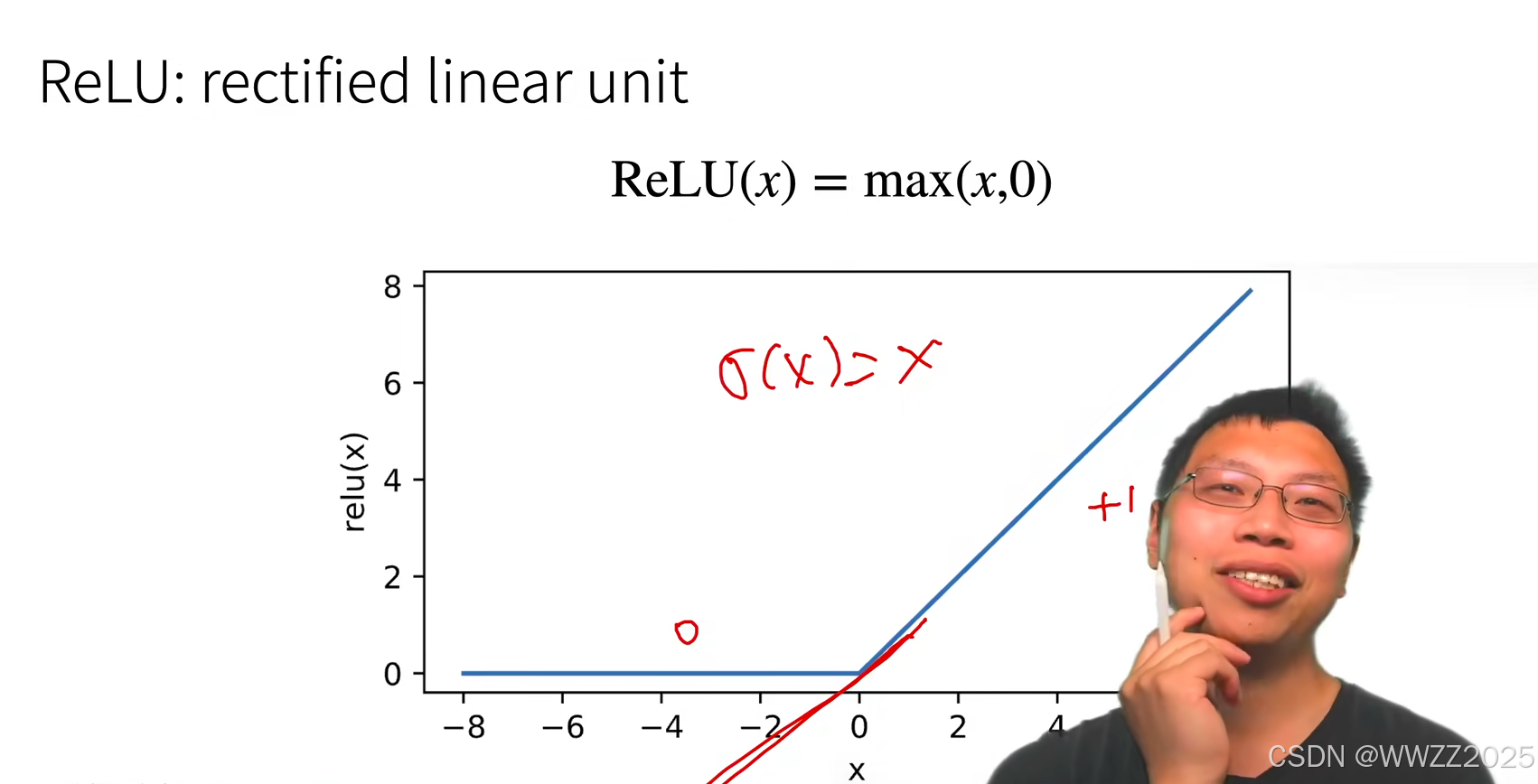
2.3 ReLU激活函数
3 多层感知机从零实现
3.1 导入库及数据集
import torch from torch import nn from d2l import torch as d2l import torch.optim as optim import matplotlib.pyplot as plt batch_size = 256 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
3.2 初始化模型参数
# 定义多层感知机模型(MLP) class MLP(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_outputs): super(MLP, self).__init__() self.flatten = nn.Flatten() # 将输入展平成一维 self.dense1 = nn.Linear(num_inputs, num_hiddens) # 第一个全连接层 self.relu = nn.ReLU() # ReLU 激活函数 self.dense2 = nn.Linear(num_hiddens, num_outputs) # 第二个全连接层 def forward(self, X): X = self.flatten(X) # 展平输入 X = self.relu(self.dense1(X)) # 第一个全连接层加 ReLU 激活 return self.dense2(X) # 第二个全连接层,输出设置隐藏层和输出层的初始参数。
3.3 模型
# 创建模型 num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_outputs = 784, 256, 10 net = MLP(num_inputs, num_hiddens, num_outputs)
3.4 损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none')此处使用交叉熵损失函数,详见5.4.4:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45728280/article/details/153778299?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
reduction参数,控制损失的汇总方式,分别为:'none','mean','sum'。其中'none'指返回每个样本的单独损失,'mean'指返回所有样本的平均损失,'sum'指返回所有样本损失的总和。
3.5 训练
# 准确度计算 def accuracy(y_hat, y): return (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item() # 评估准确率的函数 def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter): net.eval() # 切换到评估模式 metric = d2l.Accumulator(2) # 存储正确预测和总数 with torch.no_grad(): # 关闭梯度计算 for X, y in data_iter: metric.add(accuracy(net(X), y), y.size(0)) return metric[0] / metric[1] # 自定义训练函数 def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): net.train() # 切换到训练模式 # 用于保存每轮的loss和accuracy train_losses = [] train_accuracies = [] test_accuracies = [] for epoch in range(num_epochs): print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}") train_acc, train_loss = 0.0, 0.0 num_train_samples = 0 for X, y in train_iter: y_hat = net(X) # 前向传播 l = loss(y_hat, y) # 计算损失 # 将损失转换为标量 l = l.mean() # 或者 l.sum() 根据需要选择 updater.zero_grad() # 清除梯度 l.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度 updater.step() # 更新参数 # 累积准确度和损失 train_acc += accuracy(y_hat, y) train_loss += l.item() * y.size(0) num_train_samples += y.size(0) # 打印每轮训练结果 print(f" Train Loss: {train_loss / num_train_samples:.4f}, Train Accuracy: {train_acc / num_train_samples:.4f}") # 评估每个epoch结束后模型在测试集上的表现 test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter) print(f" Test Accuracy: {test_acc:.4f}") # 记录每轮的结果 train_losses.append(train_loss / num_train_samples) train_accuracies.append(train_acc / num_train_samples) test_accuracies.append(test_acc) # 返回训练过程中记录的结果 return train_losses, train_accuracies, test_accuracies # 优化器 lr = 0.1 updater = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) # 使用nn.Module的parameters()获取模型参数 # 训练 num_epochs = 10 train_losses, train_accuracies, test_accuracies = train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater)
3.6 绘制图像
# 绘制训练损失、训练准确度和测试准确度的曲线 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) # 绘制训练损失曲线 plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs + 1), train_losses, label='Train Loss', color='blue', linestyle='-', marker='o') # 绘制训练准确度曲线 plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs + 1), train_accuracies, label='Train Accuracy', color='green', linestyle='-', marker='x') # 绘制测试准确度曲线 plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs + 1), test_accuracies, label='Test Accuracy', color='red', linestyle='-', marker='s') # 设置图表的标签和标题 plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Value') plt.title('Train Loss, Train Accuracy and Test Accuracy') plt.legend() # 显示图例 plt.grid(True) # 显示网格 # 显示图形 plt.tight_layout() plt.show()
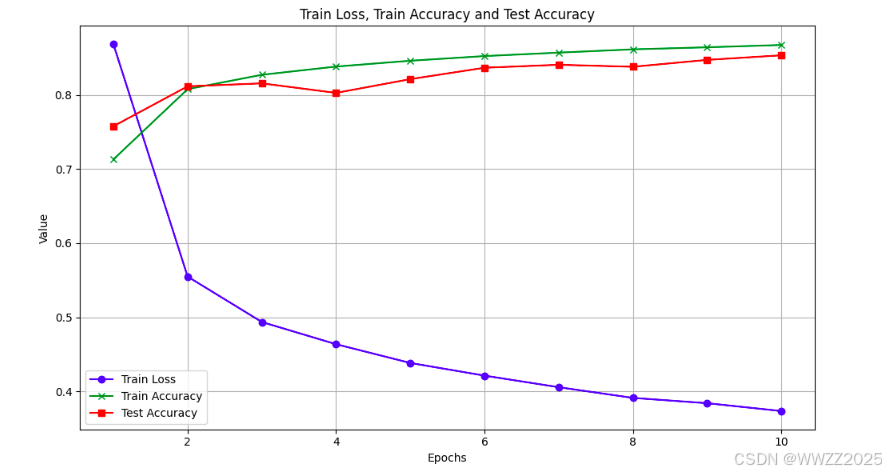
3.7 结果
Epoch 1/10 Train Loss: 0.8688, Train Accuracy: 0.7132 Test Accuracy: 0.7580 Epoch 2/10 Train Loss: 0.5549, Train Accuracy: 0.8081 Test Accuracy: 0.8119 Epoch 3/10 Train Loss: 0.4935, Train Accuracy: 0.8275 Test Accuracy: 0.8159 Epoch 4/10 Train Loss: 0.4635, Train Accuracy: 0.8386 Test Accuracy: 0.8030 Epoch 5/10 Train Loss: 0.4382, Train Accuracy: 0.8465 Test Accuracy: 0.8216 Epoch 6/10 Train Loss: 0.4211, Train Accuracy: 0.8528 Test Accuracy: 0.8370 Epoch 7/10 Train Loss: 0.4054, Train Accuracy: 0.8574 Test Accuracy: 0.8410 Epoch 8/10 Train Loss: 0.3910, Train Accuracy: 0.8619 Test Accuracy: 0.8383 Epoch 9/10 Train Loss: 0.3838, Train Accuracy: 0.8646 Test Accuracy: 0.8476 Epoch 10/10 Train Loss: 0.3733, Train Accuracy: 0.8677 Test Accuracy: 0.8538
4 多层感知机简洁实现
# 调用库 import torch from torch import nn from d2l import torch as d2l #模型 net = nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 10)) def init_weights(m): if type(m) == nn.Linear: nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01) net.apply(init_weights); #导入数据集 batch_size, lr, num_epochs = 256, 0.1, 10 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none') trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) #定义训练函数 # 自定义 train_ch3 函数(完全兼容 d2l 的写法) def train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, updater): # 定义一个精度计算函数 def accuracy(y_hat, y): return (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).float().mean().item() # 训练 for epoch in range(num_epochs): # 训练模式 net.train() total_loss, total_acc, total_num = 0.0, 0.0, 0 for X, y in train_iter: y_hat = net(X) l = loss(y_hat, y).mean() updater.zero_grad() l.backward() updater.step() total_loss += l.item() * y.size(0) total_acc += (y_hat.argmax(1) == y).float().sum().item() total_num += y.size(0) train_loss = total_loss / total_num train_acc = total_acc / total_num test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter) print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {train_loss:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, test acc {test_acc:.3f}') # 定义测试精度评估函数 def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter): net.eval() acc_sum, n = 0.0, 0 with torch.no_grad(): for X, y in data_iter: acc_sum += (net(X).argmax(dim=1) == y).float().sum().item() n += y.size(0) return acc_sum / n #训练 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) train_ch3(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, num_epochs, trainer)结果:
5 兼容性修正
5.1 安装
考虑版本兼容问题,安装兼容新版依赖的d2l版本:
pip install -U d2l==1.0.3
5.2 验证版本
在jupyter notebook中新建一个单元格,输入下面代码,查看输出。注意在D2L V1.0.3以后,
train_ch3被移除,改成了更通用的train_ch13()
import sys, d2l print(sys.executable) print(d2l.__file__) print(d2l.__version__)
5.3 测试代码
from d2l import torch as d2l import torch from torch import nn # 1. 定义模型 net = nn.Sequential( nn.Flatten(), nn.Linear(784, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 10) ) def init_weights(m): if type(m) == nn.Linear: nn.init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.01) net.apply(init_weights) # 2. 数据 batch_size, lr, num_epochs = 256, 0.1, 10 train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size) # 3. 损失函数和优化器 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(reduction='none') trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr) # 4. 显式传入 devices 参数 d2l.train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs, devices=[d2l.try_gpu()])