文章目录
后端 1 中提到如何构建 BA 问题,即同时优化所有的相机位姿和路径点,而本讲主要探讨的就是如何保证在大规模场景下 BA 的实时性
BA 的理想情况是将所有时刻的所有相机和路径点都放进 H H H 矩阵优化,但是随着时间的推移将产生大量数据,这将严重影响实时性乃至超出计算机的处理能力
为了解决此问题,有两种较为常见的方法
- 滑动窗口法:将 BA 固定在一个时间窗口,每当新的关键帧加入时,将窗口内最早的关键帧丢弃
- 共视图:仅优化与当前帧有足够共视路标点的关键帧
滑动窗口
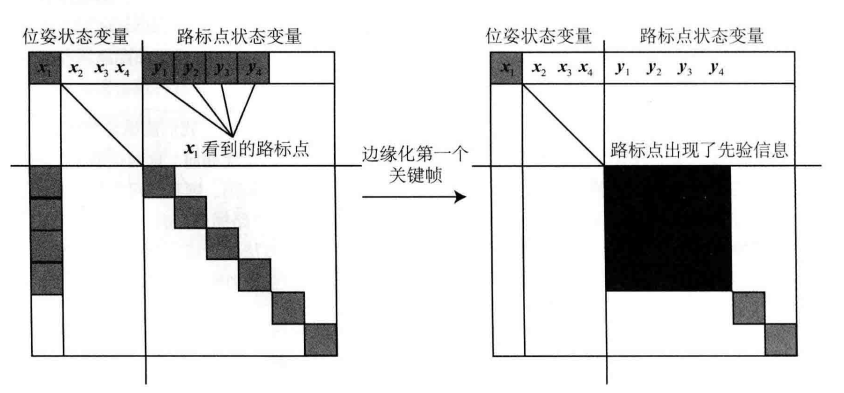
在使用滑动窗口算法的时候,当加入新的关键帧时,旧的关键帧的处理便成了问题,如果直接删除,那么这一帧的约束信息将直接消失,导致协方差估计过于乐观,降低精度。因此我们需要利用边缘化提炼出旧帧的信息保留下来
边缘化与 Schur 补
边缘化的本质是利用 Schur 补将被删除变量的信息投影到剩余变量上
回顾 BA 中的线性方程: H Δ x = g H\Delta x=g HΔx=g
H m m H m r H r m H r r \] ⋅ \[ Δ x m Δ x r \] = \[ b m b r \] \\begin{bmatrix} H_{mm}\&H_{mr}\\\\H_{rm}\&H_{rr} \\end{bmatrix} \\cdot \\begin{bmatrix} \\Delta x_{m}\\\\ \\Delta x_{r} \\end{bmatrix}= \\begin{bmatrix} b_{m}\\\\b_{r} \\end{bmatrix} \[HmmHrmHmrHrr\]⋅\[ΔxmΔxr\]=\[bmbr
- x m x_{m} xm :将被边缘化的变量
- x r x_{r} xr :保留的剩余变量
利用高斯消元得到关于 Δ x \Delta x Δx 的方程:
( H r r − H r m H m m − 1 H m r ) ⏟ H n e w Δ x r = b r − H r m H m m − 1 b m \underbrace{(H_{rr}-H_{rm}H_{mm}^{-1}H_{mr})}{H{new}}\Delta x_{r}=b_{r}-H_{rm}H^{-1}{mm}b{m} Hnew (Hrr−HrmHmm−1Hmr)Δxr=br−HrmHmm−1bm
H n e w H_{new} Hnew 即边缘化后剩余变量 x r x_{r} xr 的新信息矩阵
传递对象: - 滑动窗口内较新的关键帧:如果新帧与被边缘化的旧帧观测到了相同的路标点,或者有直接的里程计约束,那么旧帧的信息会作为先验信息传递给新帧
- 滑动窗口内的路标点:更新被边缘化的旧帧观测的路标点位置
| 特性 | BA | 边缘化 |
|---|---|---|
| 场景 | 求解 H Δ x = g H\Delta x=g HΔx=g | 移除旧帧并保留信息 |
| 消除变量 | 路标点 Δ x p \Delta x_{p} Δxp | 旧关键帧 Δ x m \Delta x_{m} Δxm |
| 保留变量 | 相机位姿 Δ x e \Delta x_{e} Δxe | 剩余帧+路标 Δ x r \Delta x_{r} Δxr |
| Schur补 | S = B − E C − 1 E T S=B-EC^{-1}E^T S=B−EC−1ET | H n e w = H r r − H r m H m m − 1 H m r H_{new}=H_{rr}-H_{rm}H^{-1}{mm}H{mr} Hnew=Hrr−HrmHmm−1Hmr |
| 目的 | 加速计算,求解相机位姿 | 信息传递,将旧帧的约束传给新帧 |
S S S 矩阵其实就是边缘化掉路标点的相机位姿信息矩阵( H n e w H_{new} Hnew)
稀疏性的破坏(Fill in)
让我们回忆一下后端 1 中提到的 
H = [ B E E T C ] H=\begin{bmatrix} B & E \\ E^T & C \end{bmatrix} \\ H=[BETEC]
其中 C 矩阵是对角块矩阵,因为路径点与路径点之间并无联系,所以仅有对角上用 3 × 3 3\times 3 3×3 矩阵存储路径点的信息矩阵,其余点都为0
对于对角矩阵 C i i C_{ii} Cii ,其存储的是所有相机关于该路标点位置的二阶导数之和 ,物理意义上,它描述的是该路标点的确定程度
路标点之间的无关性正是 C 矩阵稀疏性的来源,基于这点,BA 才能利用 Schur 消元加速计算
当我们使用边缘化移除旧帧 T o l d T_{old} Told 时:
- T o l d T_{old} Told 同时观测到的所有路径点,都与 T o l d T_{old} Told 存在着约束
- 当我们边缘化 T o l d T_{old} Told 时,Schur 补会将这些点都联系起来
- 这意味着原先互不相关的路径点之间,产生了直接的数学联系
这将使得 C 矩阵中原先非对角的元素不再为 0 ,C 矩阵变成了稠密矩阵,在下一次 BA 过程中,无法利用 C 矩阵的稀疏性加速计算
位姿图
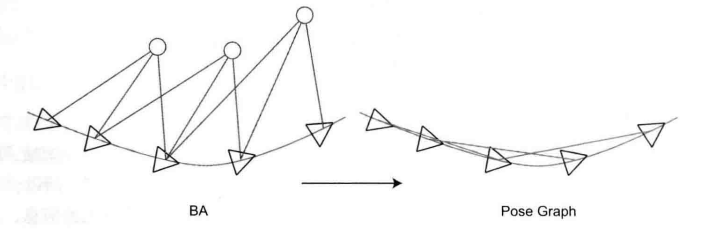
如果不希望处理复杂的边缘化,或者需要进行大范围的全局调整,可以采用位姿图优化。
位姿图优化的核心思想就是不再优化 BA 中的路标点,而是仅把它们看成对姿态节点的约束
位姿图优化
位姿图中的节点标示相机位姿,以 T 1 , ⋯ , T n T_{1},\cdots,T_{n} T1,⋯,Tn 表示,边则是两个位姿节点之间的相对运动估计。
假设我们估计 T i T_{i} Ti 和 T j T_{j} Tj 之间的一个相对运动 T i j T_{ij} Tij ,表达式如下
T i j = T i − 1 T j T_{ij}=T_{i}^{-1}T_{j} Tij=Ti−1Tj
或者写成李代数形式( ∘ \circ ∘ 表示"在李群上做逆和乘法,对应到李代数上的运算", ∨ ^\vee ∨ 表示矩阵转向量)
Δ ξ i j = ξ i − 1 ∘ ξ j = ln ( T i − 1 T j ) ∨ \Delta \xi_{ij}=\xi_{i}^{-1}\circ\xi_{j}=\ln(T_{i}^{-1}T_{j})^\vee Δξij=ξi−1∘ξj=ln(Ti−1Tj)∨
该等式不会严格成立,所以我们还要引入最小二乘,先构建误差项 e i j e_{ij} eij
e i j = ln ( T i j − 1 T i − 1 T j ) ∨ e_{ij}=\ln(T^{-1}{ij}T^{-1}{i}T_{j})^\vee eij=ln(Tij−1Ti−1Tj)∨
- T i j − 1 T_{ij}^{-1} Tij−1 :两个相机之间的相对运动测量值
- T i , T j T_{i},T_{j} Ti,Tj :两个相机在世界坐标系下的估计位姿
理想情况下, T i j = T i − 1 T j T_{ij}=T_{i}^{-1}T_{j} Tij=Ti−1Tj
李群和李代数中提到过,李群无法直接做减法,这里用"乘逆"来表示减法如果估计没有偏差, T i j − 1 ⋅ ( T i − 1 T j ) = I T_{ij}^{-1}\cdot(T_{i}^{-1}T_{j})=I Tij−1⋅(Ti−1Tj)=I
反之则是得到一个残差矩阵
要优化的变量有两个: ξ i \xi_{i} ξi 和 ξ j \xi_{j} ξj ,因此我们要求 e i j e_{ij} eij 关于这两个变量的导数,给 T i T_{i} Ti 和 T j T_{j} Tj 各自左乘扰动 δ ξ i \delta\xi_i δξi 和 δ ξ j \delta\xi_j δξj ,此时误差变为 ( ( A B ) − 1 = B − 1 A − 1 (AB)^{-1}=B^{-1}A^{-1} (AB)−1=B−1A−1)
e ^ i j = ln ( T i j − 1 T i − 1 exp ( − δ ξ i ∧ ) exp ( δ ξ j ∧ ) ) ∨ \hat{e}{ij}=\ln\left(T{ij}^{-1}T_{i}^{-1}\exp\left(-\delta\xi_{i}^\wedge\right)\exp(\delta\xi_{j}^\wedge)\right)^\vee e^ij=ln(Tij−1Ti−1exp(−δξi∧)exp(δξj∧))∨
为了利用李群和李代数,我们需要将式子化为诸如 ln ( A ⋅ exp ( δ ∧ ) ) ∨ \ln(A\cdot \exp(\delta^\wedge))^\vee ln(A⋅exp(δ∧))∨ 的形式
定义 Δ ξ = d e f δ ξ j − δ ξ i \Delta\xi \stackrel{def}{=}\delta\xi_{j}-\delta\xi_{i} Δξ=defδξj−δξi
先进行线性近似 ( exp ( A ) exp ( B ) = exp ( A + B ) ) (\exp(A)\exp(B)=\exp(A+B)) (exp(A)exp(B)=exp(A+B)),得到
e ^ i j ≈ ln ( T i j − 1 T i − 1 exp ( Δ ξ ∧ ) T j ) ∨ \hat{e}{{ij}}\approx\ln\left(T{ij}^{-1}T_{i}^{-1}\exp\left(\Delta\xi^\wedge\right)T_{j}\right)^\vee e^ij≈ln(Tij−1Ti−1exp(Δξ∧)Tj)∨
在下一步推导之前,我们还需要了解一下**共轭和伴随性质**
不过 T i − 1 exp ( ( Δ ξ ) ∧ ) T j T_{i}^{-1}\exp\left((\Delta\xi)^\wedge\right)T_{j} Ti−1exp((Δξ)∧)Tj 并不是一个共轭式子,只是一个约束链,因为共轭式子的要求是左右两侧的矩阵必须是互为逆的同一位姿,但这里是不同时刻的两个位姿
先来剖析一下这个式子:
P j ⏟ j 坐标系 → T j P W ⏟ 世界坐标系 → exp ( Δ ξ ∧ ) P W ′ ⏟ 施加扰动后 → T i − 1 P i ⏟ i 坐标系 \underbrace{ P_{j} }{ j~\text{}{坐标系} } \xrightarrow{T{j}} \underbrace{ P_{W} }{ \text{世界坐标系} } \xrightarrow{\exp(\Delta\xi^\wedge)}\underbrace{ P{W}' }{ \text{施加扰动后} } \xrightarrow{T{i}^{-1}} \underbrace{ P_{i} }_{ i~\text{坐标系} } j 坐标系 PjTj 世界坐标系 PWexp(Δξ∧) 施加扰动后 PW′Ti−1 i 坐标系 Pi
这显然不满足条件,因为误差项应当是在 j 坐标系下的,所以还要利用伴随性质纠正坐标系转换
已知:
exp ( ξ ∧ ) T = T exp ( ( A d ( T − 1 ) ξ ) ∧ ) \exp(\xi^\wedge)T=T\exp\left((Ad(T^{-1})\xi)^\wedge\right) exp(ξ∧)T=Texp((Ad(T−1)ξ)∧)
此时可以凑出标准的 BCH 形式
e ^ i j = ln ( T i j − 1 T i − 1 T j ⏟ E i j (原误差) ⋅ exp ( ( A d ( T j − 1 ) Δ ξ ) ∧ ⏟ 转换后扰动 ) ) ∨ \hat{e}{ij}=\ln\left(\underbrace{ T{ij}^{-1}T_{i}^{-1}T_{j} }{ E{ij} \text{(原误差)}}\cdot \exp\left(\underbrace{ (Ad(T_{j}^{-1})\Delta \xi)^\wedge}_{ \text{转换后扰动} }\right)\right)^\vee e^ij=ln Eij(原误差) Tij−1Ti−1Tj⋅exp 转换后扰动 (Ad(Tj−1)Δξ)∧ ∨
根据 S E ( 3 ) SE(3) SE(3) 上的 BCH 近似:
ln ( A ⋅ exp ( δ ∧ ) ) ∨ ≈ ln ( A ) ∨ + J r − 1 ( ln ( A ) ∨ ) ⋅ δ \ln(A\cdot \exp(\delta^\wedge))^\vee \approx \ln(A)^\vee+J_{r}^{-1}(\ln(A)^\vee)\cdot\delta ln(A⋅exp(δ∧))∨≈ln(A)∨+Jr−1(ln(A)∨)⋅δ
代入得到最终的线性化误差公式:
e ^ i j ≈ e i j + J r − 1 ( e i j ) ⋅ A d ( T j − 1 ⋅ Δ ξ ) \hat{e}{ij}\approx e{ij}+J_{r}^{-1}(e_{ij})\cdot Ad(T_{j}^{-1}\cdot\Delta \xi) e^ij≈eij+Jr−1(eij)⋅Ad(Tj−1⋅Δξ)
展开得到
e ^ i j ≈ e i j + J r − 1 ( e i j ) A d ( T j − 1 ) ⋅ δ ξ j ⏟ 对 j 的导数项 − J r − 1 ( e i j ) A d ( T j − 1 ) ⋅ δ ξ i ⏟ 对 i 的导数项 \hat{e}{ij}\approx e{ij}+\underbrace{ J_{r}^{-1}(e_{ij})Ad(T^{-1}{j})\cdot\delta \xi{j} }{ \text{对} j \text{的导数项} }-\underbrace{ J{r}^{-1}(e_{ij})Ad(T_{j}^{-1})\cdot\delta \xi_{i} }_{ \text{对 } i \text{ 的导数项} } e^ij≈eij+对j的导数项 Jr−1(eij)Ad(Tj−1)⋅δξj−对 i 的导数项 Jr−1(eij)Ad(Tj−1)⋅δξi
于是我们得到了误差关于两个位姿的雅可比矩阵
- 对 T i T_{i} Ti 的雅可比:
∂ e i j ∂ δ ξ i = − J r − 1 ( e i j ) ⋅ A d ( T j − 1 ) \frac{\partial e_{ij}}{\partial\delta \xi_{i}}=-J_{r}^{-1}(e_{ij})\cdot Ad(T_{j}^{-1}) ∂δξi∂eij=−Jr−1(eij)⋅Ad(Tj−1) - 对 T j T_{j} Tj 的雅可比: ∂ e i j ∂ δ ξ j = J r − 1 ( e i j ) ⋅ A d ( T j − 1 ) \frac{\partial e_{ij}}{\partial\delta \xi_{j}}=J_{r}^{-1}(e_{ij})\cdot Ad(T_{j}^{-1}) ∂δξj∂eij=Jr−1(eij)⋅Ad(Tj−1)
由于 s e ( 3 ) \mathfrak{se}(3) se(3) 上的左右雅可比形式过于复杂,所以通常会取近似值,当误差接近于 0 时,我们可以近似其为 I I I 或
J r − 1 ( e i j ) ≈ I + 1 2 [ ϕ e ∧ ρ e ∧ 0 ϕ e ∧ ] J_{r}^{-1}(e_{ij}) \approx I + \frac{1}{2}\begin{bmatrix}\phi_{e}^\wedge&\rho_{e}^\wedge\\0&\phi_{e}^\wedge\end{bmatrix} Jr−1(eij)≈I+21[ϕe∧0ρe∧ϕe∧]
不用过于担心近似引进的误差,因为在迭代算法里,我们其实需求的不是实际精确的值,而是一个优化方向,而且随着迭代的推进,误差减小的时候,雅可比矩阵也会靠近我们近似的 I I I
g2o 与位姿图优化
\[g2o入门\]
原生 g2o 代码实例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Geometry>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <sophus/so3.hpp>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/dense/linear_solver_dense.h>
#include <g2o/types/slam3d/vertex_se3.h>
#include <g2o/types/slam3d/edge_se3.h>
int main()
{
// 1. 数据生成
// 半径 10 米的圆周轨迹,每步走一度
std::vector<Eigen::Isometry3d> poses;
double radius = 10.0;
for (int i = 0; i < 360; i++)
{
double theta = i * M_PI / 180.0;
// 位置
Eigen::Vector3d trans(radius * cos(theta), radius * sin(theta), 0);
// 姿态
Eigen::Quaterniond q;
q = Eigen::AngleAxisd(theta + M_PI_2, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
Eigen::Isometry3d pose = Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity();
pose.rotate(q);
pose.pretranslate(trans);
poses.push_back(pose);
}
// 2. 构建 g2o 优化器
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 6>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverDense<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
auto solver = std::make_unique<g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg>(
std::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(std::make_unique<LinearSolverType>())
);
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver.release());
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
// 3. 添加位姿顶点
// 添加噪声
Eigen::Isometry3d current_pose = poses[0];
// 随机数生成器
double trans_noise = 0.1; // 平移噪声标准差
double rot_noise = 0.01; // 旋转噪声标准
for (int i = 0; i < poses.size(); i++)
{
g2o::VertexSE3* v = new g2o::VertexSE3();
v->setId(i);
if (i == 0)
{
v->setEstimate(current_pose);
v->setFixed(true); // 固定第一个位姿
}
else
{
// 计算相对运动真实值
Eigen::Isometry3d relative_motion = poses[i - 1].inverse() * poses[i];
// 添加噪声
Eigen::Vector3d noise_trans = Eigen::Vector3d::Random() * trans_noise;
Eigen::Vector3d noise_rot = Eigen::Vector3d::Random() * rot_noise;
Eigen::Quaterniond noise_q = Sophus::SO3d::exp(noise_rot).unit_quaternion();
Eigen::Isometry3d noisy_relative_motion = Eigen::Isometry3d::Identity();
noisy_relative_motion.rotate(noise_q * relative_motion.rotation());
noisy_relative_motion.pretranslate(relative_motion.translation() + noise_trans);
// 更新当前位姿
current_pose = current_pose * noisy_relative_motion;
v->setEstimate(current_pose);
// 添加边
auto edge = std::make_unique<g2o::EdgeSE3>();
edge->setVertex(0, optimizer.vertex(i - 1));
edge->setVertex(1, v);
edge->setMeasurement(noisy_relative_motion);
// 信息矩阵
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> information = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Identity();
information.block<3,3>(0, 0) *= 1.0 / (trans_noise * trans_noise);
information.block<3,3>(3, 3) *= 1.0 / (rot_noise * rot_noise);
edge->setInformation(information);
optimizer.addEdge(edge.release());
}
optimizer.addVertex(v);
}
auto* last_vertex = static_cast<g2o::VertexSE3*>(optimizer.vertex(359));
Eigen::Vector3d end_error = last_vertex->estimate().translation() - poses[359].translation();
std::cout << "Before optimization: End pose error distance = "
<< end_error.norm()
<< " m" << std::endl;
// 添加回环边
g2o::EdgeSE3* loop_edge = new g2o::EdgeSE3();
loop_edge->setVertex(0, optimizer.vertex(359)); // 回环到第一个顶点
loop_edge->setVertex(1, optimizer.vertex(0));
Eigen::Isometry3d loop_measurement = poses[359].inverse() * poses[0];
loop_edge->setMeasurement(loop_measurement);
Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> loop_information = Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Identity() * 1000.0;
loop_edge->setInformation(loop_information);
optimizer.addEdge(loop_edge);
// 4. 优化
std::cout << "Start optimization" << std::endl;
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(100);
auto* new_last_vertex = static_cast<g2o::VertexSE3*>(optimizer.vertex(359));
Eigen::Vector3d new_end_error = new_last_vertex->estimate().translation() - poses[359].translation();
std::cout << "After optimization: End pose error distance = "
<< new_end_error.norm()
<< " m" << std::endl;
optimizer.save("pose_graph_result.g2o");
}效果图如下:

李代数代码实例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Geometry>
#include <sophus/se3.hpp>
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/eigen/linear_solver_eigen.h>
#include <g2o/core/factory.h>
#include <g2o/stuff/command_args.h>
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 6> Matrix6d;
typedef Eigen::Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d;
// J_R^{-1} 的近似
Matrix6d JRinv(const Sophus::SE3d& e)
{
Matrix6d J;
J.block(0, 0, 3, 3) = Sophus::SO3d::hat(e.so3().log());
J.block(0, 3, 3, 3) = Sophus::SO3d::hat(e.translation());
J.block(3, 0, 3, 3) = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();
J.block(3, 3, 3, 3) = Sophus::SO3d::hat(e.so3().log());
J = J * 0.5 + Matrix6d::Identity();
return J;
}
class VertexSE3LieAlgebra : public g2o::BaseVertex<6, Sophus::SE3d>
{
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override
{
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d();
}
virtual void oplusImpl(const double* update) override
{
Vector6d update_eigen;
update_eigen << update[0], update[1], update[2], update[3], update[4], update[5];
_estimate = Sophus::SE3d::exp(update_eigen) * _estimate;
}
virtual bool read(std::istream& in) override
{
double data[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
in >> data[i];
setEstimate(Sophus::SE3d(
Eigen::Quaterniond(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]).normalized(),
Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])
));
return true;
}
virtual bool write(std::ostream& os) const override
{
Eigen::Quaterniond q = _estimate.unit_quaternion();
os << _estimate.translation().transpose() << " ";
os << q.x() << " " << q.y() << " " << q.z() << " " << q.w() << std::endl;
return true;
}
};
//
class EdgeSE3LieAlgebra : public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<6, Sophus::SE3d, VertexSE3LieAlgebra, VertexSE3LieAlgebra> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW
virtual void computeError() override
{
Sophus::SE3d v1 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra*>(_vertices[0]))->estimate();
Sophus::SE3d v2 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra*>(_vertices[1]))->estimate();
_error = (_measurement.inverse() * (v1.inverse() * v2)).log();
}
// 雅可比计算( J_r^{-1} \approx I)
virtual void linearizeOplus() override
{
Sophus::SE3d v2 = (static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra*>(_vertices[1]))->estimate();
Matrix6d J = JRinv(Sophus::SE3d::exp(_error));
J = J * v2.inverse().Adj();
_jacobianOplusXi = -J;
_jacobianOplusXj = J;
}
virtual bool read(std::istream& in) override
{
double data[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
in >> data[i];
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
q.normalize();
setMeasurement(Sophus::SE3d(
q,
Eigen::Vector3d(data[0], data[1], data[2])
));
for (int i = 0; i < information().rows(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < information().cols(); j++)
{
in >> information()(i, j);
// 保持对称性
if (i != j)
{
information()(j, i) = information()(i, j);
}
}
}
return true;
}
virtual bool write(std::ostream& os) const override
{
VertexSE3LieAlgebra *v1 = static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra*>(_vertices[0]);
VertexSE3LieAlgebra *v2 = static_cast<VertexSE3LieAlgebra*>(_vertices[1]);
Eigen::Quaterniond q = _measurement.unit_quaternion();
os << _measurement.translation().transpose() << " ";
os << q.x() << " " << q.y() << " " << q.z() << " " << q.w() << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < information().rows(); ++i)
{
for (int j = i; j < information().cols(); ++j)
{
os << information()(i, j) << " ";
}
}
os << std::endl;
return true;
}
};
int main()
{
// 1. 读取位姿图
std::fstream fin("../example/sphere.g2o");
if (!fin)
{
std::cerr << "File not found." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 2. 构建优化器
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<6, 6>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverEigen<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType;
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
std::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(std::make_unique<LinearSolverType>())
);
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer;
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver);
optimizer.setVerbose(true);
// 3. 从文件中加载顶点和边
int vertex_count = 0, edge_count = 0;
while (!fin.eof())
{
std::string name;
fin >> name;
if (name == "VERTEX_SE3:QUAT")
{
int idx = 0;
double data[7];
fin >> idx;
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++)
fin >> data[i];
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
q.normalize();
Eigen::Vector3d t(data[0], data[1], data[2]);
Sophus::SE3d pose(q, t);
VertexSE3LieAlgebra* v = new VertexSE3LieAlgebra();
v->setId(idx);
v->setEstimate(pose);
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_count++;
if (idx == 0)
v->setFixed(true); // 固定第一个节点
}
else if (name == "EDGE_SE3:QUAT")
{
int idx1, idx2;
fin >> idx1 >> idx2;
double data[7];
for (int i = 0; i < 7; ++i)
fin >> data[i];
Eigen::Quaterniond q(data[6], data[3], data[4], data[5]);
q.normalize();
Eigen::Vector3d t(data[0], data[1], data[2]);
Sophus::SE3d measurement(q, t);
Matrix6d information = Matrix6d::Zero();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j < 6; j++)
{
fin >> information(i, j);
if (i != j)
information(j, i) = information(i, j);
}
}
EdgeSE3LieAlgebra* e = new EdgeSE3LieAlgebra();
e->setVertex(0, optimizer.vertex(idx1));
e->setVertex(1, optimizer.vertex(idx2));
e->setMeasurement(measurement);
e->setInformation(information);
optimizer.addEdge(e);
edge_count++;
}
if (!fin.good())
break;
}
std::cout << "Read total " << vertex_count << " vertices, " << edge_count << " edges." << std::endl;
// 4. 优化
std::cout << "Start optimization" << std::endl;
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(100);
// 5. 保存结果
optimizer.save("sphere_se3_result.g2o");
}
G2O_REGISTER_TYPE_NAME("VERTEX_SE3:QUAT", VertexSE3LieAlgebra);
G2O_REGISTER_TYPE_NAME("EDGE_SE3:QUAT", EdgeSE3LieAlgebra);优化前
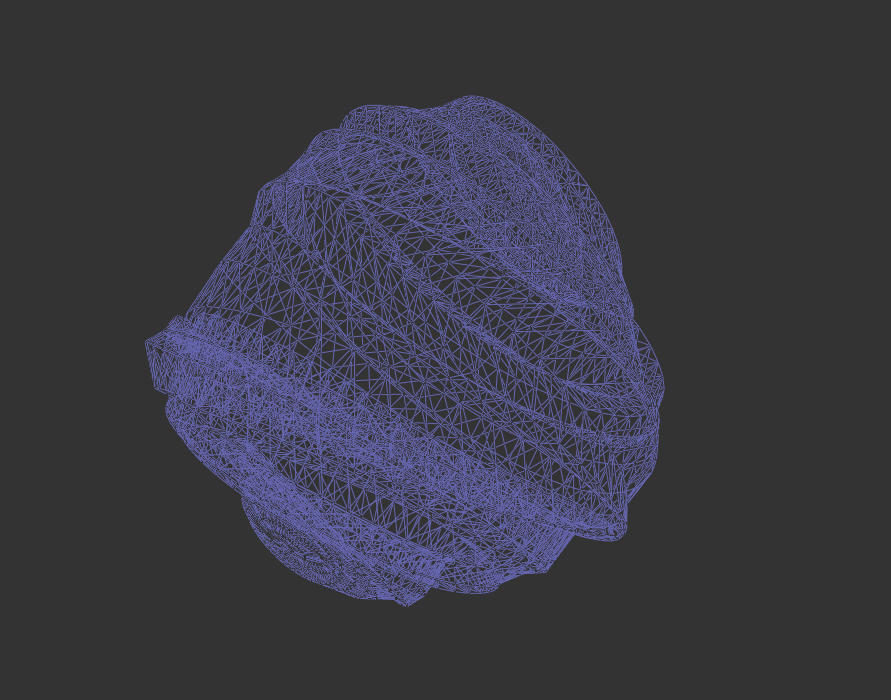
优化后