前文RANSAC算法------看完保证你理解中已经阐述了关于RANSAC算法的原理以及示例。
在许多含有噪声和异常点outliers 的数据拟合任务中,普通最小二乘法容易被异常点拉偏。RANSAC 可以在存在外点时稳健拟合,但在 near-outliers 情况下,它可能被误收内点,导致模型偏移。
MSAC(M-Estimator Sample Consensus) 是 RANSAC 的扩展,通过 残差代价 选择模型,而不仅仅依赖内点数量,从而获得更精确、稳定的拟合结果。
1. MSAC 算法详解
1.1 基本思想
MSAC 是 RANSAC 的自然扩展版本,核心目标是:
在含有外点的数据中,找到一组模型参数,使得整体残差代价最小,而不仅仅是最大化内点数量。
MSAC 的主要创新点在于 代价函数:
Cost = ∑ i = 1 N ρ ( e i ) \text{Cost} = \sum_{i=1}^{N} \rho(e_i) Cost=i=1∑Nρ(ei)
其中:
- e i e_i ei 为第 i i i 个数据点到模型的残差;
- ρ ( e i ) \rho(e_i) ρ(ei) 为 M-估计损失函数:
ρ ( e i ) = { e i 2 , if e i < threshold threshold 2 , if e i ≥ threshold \rho(e_i) = \begin{cases} e_i^2, & \text{if } e_i < \text{threshold} \\ \text{threshold}^2, & \text{if } e_i \geq \text{threshold} \end{cases} ρ(ei)={ei2,threshold2,if ei<thresholdif ei≥threshold
相比 RANSAC只计算内点数量,MSAC 将内点残差平方和阈值外点固定罚值都纳入考量,使得模型选择更加精细。
1.2 核心步骤
- 随机采样最小样本集
- 拟合模型
- 计算代价:内点残差平方,超出阈值点固定惩罚
- 更新最优模型:代价最小
- 重复迭代:直到达到最大迭代次数或置信度
可以理解为:RANSAC 关注"数量",MSAC 关注"质量"。
1.3 MSAC 与 RANSAC 对比
| 特性 | RANSAC | MSAC |
|---|---|---|
| 模型评估 | 内点数量 | 残差代价(M-估计) |
| 对 near-outliers 敏感 | 容易拉偏 | 稳健,可减小偏移 |
| 优势场景 | 外点比例高、模型简单 | 多模型竞争、复杂噪声场景 |
| 适用性 | 快速粗略估计 | 高精度鲁棒拟合 |
1.4 应用场景
MSAC 在计算机视觉和机器人领域非常实用:
- 相机标定:拟合内外参模型,剔除误匹配点
- 基础矩阵 / 单应性矩阵估计:点对中存在噪声和外点
- 点云拟合:3D 平面或曲面拟合,剔除异常点
- 自动驾驶:车道线或地面平面拟合,噪声点和遮挡点可控
- SLAM / SfM:关键点匹配中剔除错误匹配
MSAC 适合任何需要鲁棒拟合、关注模型整体残差而不仅仅是内点数量的场景。
1.5 优劣势
优点:
- 在 near-outliers 情况下保持稳定
- 模型拟合更贴近真实分布
- 对残差大小敏感,可精细选择最优模型
缺点:
- 相比 RANSAC 计算稍复杂,需要累积残差代价
- 对阈值敏感,需要合理设置
- 当外点极端大时,MSAC 和 RANSAC 差异不明显
总结:MSAC 是 RANSAC 的"进化版",更关注拟合质量,非常适合高精度与噪声复杂的任务。
2. 可视化示例
我们用一个简单的二维线性拟合实验展示 RANSAC 和 MSAC 的差异:
数据特点
- 主直线:
y = 2.5x - 1.0 - 内点:添加小噪声
- near-outliers:数量较多、略偏离真实直线,接近 RANSAC 阈值
3. Python3 完整示例(WSL 可保存图片)
python
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use("Agg")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 固定随机种子
np.random.seed(42)
random.seed(42)
# 数据生成
def generate_data():
X = np.linspace(0, 10, 60)
y_true = 2.5 * X - 1.0
y_inliers = y_true + np.random.normal(0, 0.3, size=X.shape)
X_near = np.linspace(0, 10, 40)
y_near = 2.5 * X_near - 1.0 + np.random.normal(1.5, 0.5, size=X_near.shape)
X_all = np.concatenate([X, X_near])
y_all = np.concatenate([y_inliers, y_near])
points = list(zip(X_all, y_all))
return points, X_all, y_all, y_true
# 拟合直线
def fit_line(points):
xs = np.array([p[0] for p in points])
ys = np.array([p[1] for p in points])
a, b = np.polyfit(xs, ys, 1)
return a, b
# RANSAC
def ransac(points, iterations=200, threshold=2.0):
best_model = None
best_inliers = []
for _ in range(iterations):
sample = random.sample(points, 2)
a, b = fit_line(sample)
inliers = [(x, y) for x, y in points if abs(y - (a*x + b)) < threshold]
if len(inliers) > len(best_inliers):
best_inliers = inliers
best_model = (a, b)
return best_model, best_inliers
# MSAC
def msac(points, iterations=200, threshold=2.0):
best_model = None
best_cost = float("inf")
for _ in range(iterations):
sample = random.sample(points, 2)
a, b = fit_line(sample)
cost = sum((y - (a*x + b))**2 if abs(y-(a*x+b))<threshold else threshold**2
for x, y in points)
if cost < best_cost:
best_cost = cost
best_model = (a, b)
return best_model, best_cost
# MSE评估
def mse(model, points):
a, b = model
return np.mean([(y - (a*x + b))**2 for x, y in points])
# 主程序
if __name__ == "__main__":
points, X_all, y_all, y_true = generate_data()
ransac_model, ransac_inliers = ransac(points)
msac_model, msac_cost = msac(points)
print("=== Model parameters ===")
print("True line: y = 2.5x - 1.0")
print(f"RANSAC line: y = {ransac_model[0]:.3f}x + {ransac_model[1]:.3f}")
print(f"MSAC line: y = {msac_model[0]:.3f}x + {msac_model[1]:.3f}")
print("\n=== Error comparison ===")
print(f"RANSAC MSE: {mse(ransac_model, points):.4f}")
print(f"MSAC MSE: {mse(msac_model, points):.4f}")
# 可视化保存
plt.figure(figsize=(8,5))
plt.scatter(X_all, y_all, s=10, color="gray", label="data")
X_plot = np.linspace(0,10,100)
plt.plot(X_plot, 2.5*X_plot-1, "k--", label="Ground truth")
plt.plot(X_plot, ransac_model[0]*X_plot + ransac_model[1], "b", label="RANSAC")
plt.plot(X_plot, msac_model[0]*X_plot + msac_model[1], "r", label="MSAC")
plt.legend()
plt.title("RANSAC vs MSAC (near-outliers visible)")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("ransac_vs_msac.png", dpi=150)
plt.close()
print("\nFigure saved to: ransac_vs_msac.png")4. 运行效果
终端输出示例:
=== Model parameters ===
True line: y = 2.5x - 1.0
RANSAC line: y = 2.549x + -1.312
MSAC line: y = 2.504x + -1.072
=== Error comparison ===
RANSAC MSE: 0.6098
MSAC MSE: 0.5986
Figure saved to: ransac_vs_msac.png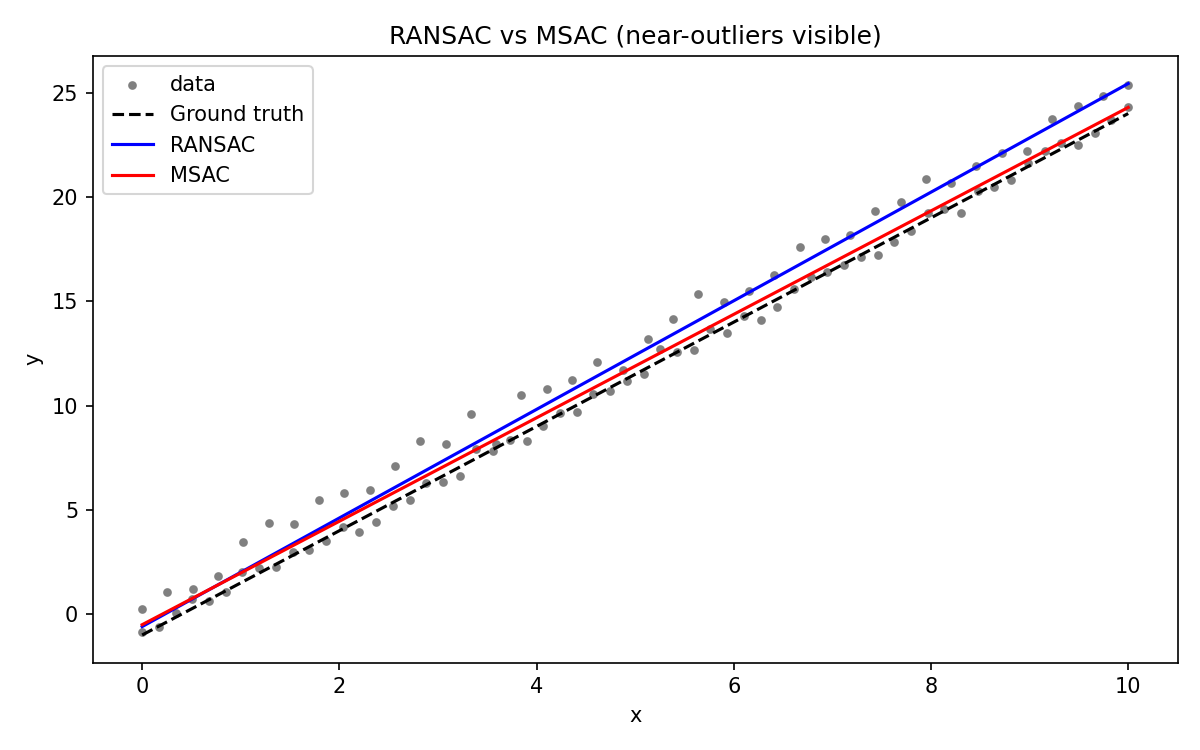
灰色散点:数据
黑色虚线:真实直线
蓝色:RANSAC(被 near-outliers 拉偏)
红色:MSAC(贴近真实线)
5. 总结
1. MSAC 优势:
- 在 near-outliers 或多模型竞争场景下稳健
- 不仅考虑内点数量,还关注残差平方
2. RANSAC 优势:
-
简单快速
-
对内点占比高的任务已足够
3.可视化实验:
-
near-outliers 会显著拉偏 RANSAC
-
MSAC 拟合更接近真实模型
-
MSAC 是 RANSAC 的自然升级,适用于自动驾驶、点云拟合、相机标定等高精度任务。