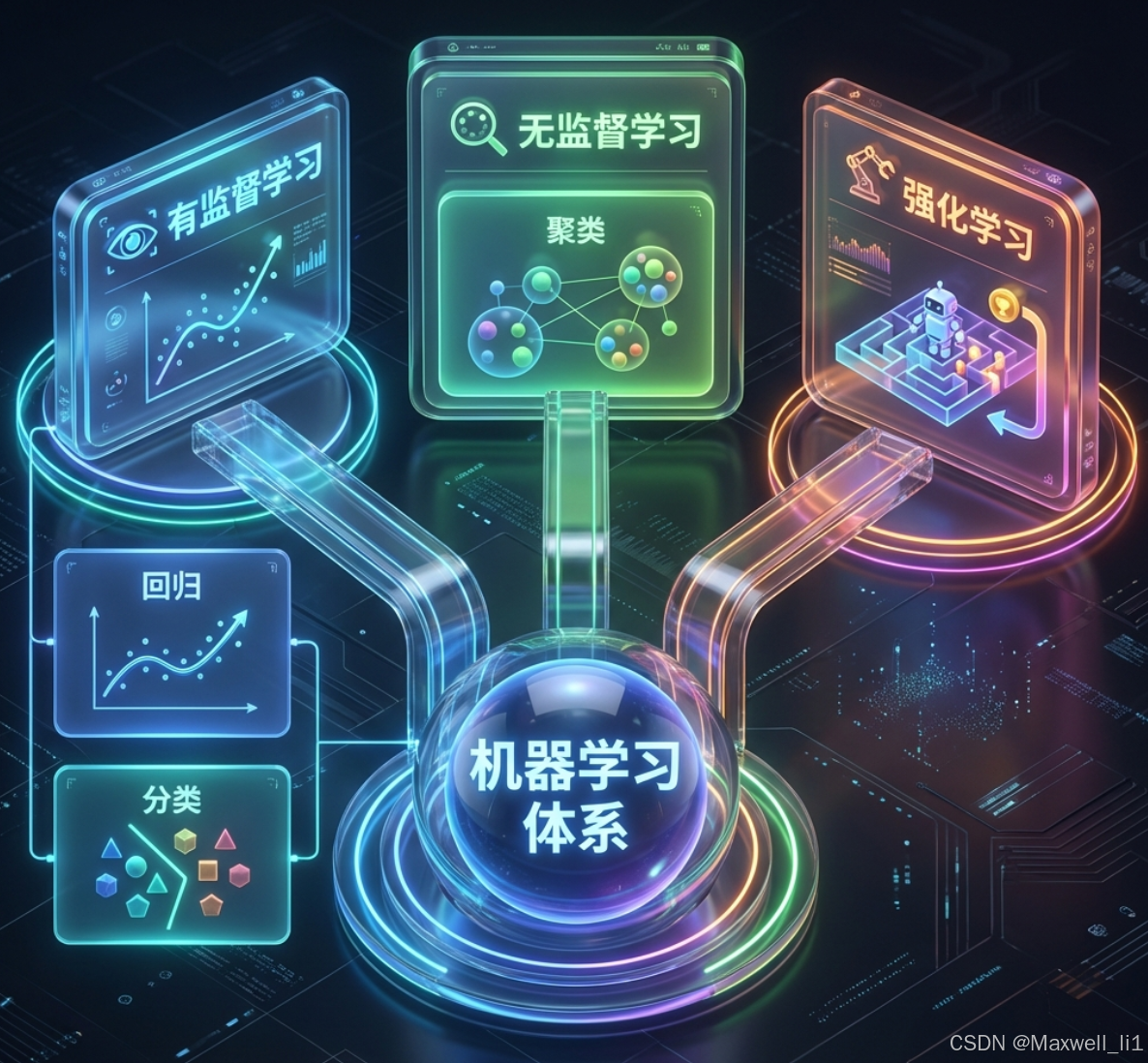
机器学习知识点梳理
• 回归模型:线性回归、决策树、SVM(可以,效果差)
• 分类模型:逻辑回归、决策树、SVM、朴素贝叶斯(只能分类)
• 聚类模型:kmeans(基于原型)、DBSCAN(基于密度)、凝聚层次(基于层次)
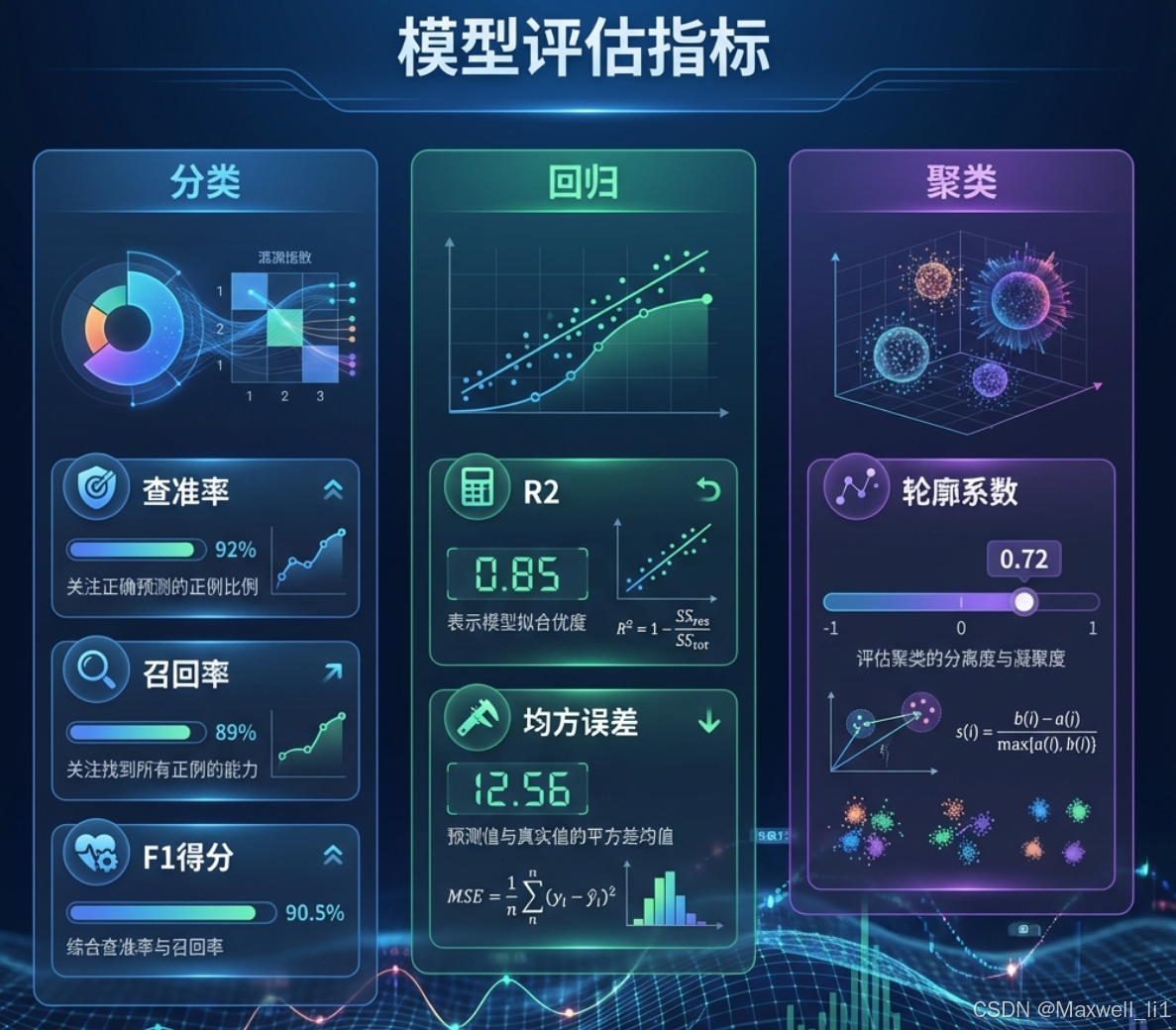
• 评估方法:
◦ 回归问题:R2(综合指标)、均方误差(损失函数)
◦ 分类问题:查准率(评估误检)、召回率(评估漏检)、F1(综合评估前两者)
◦ 聚类问题:轮廓系数

第一部分:常用导入包及其作用
1. 核心科学计算库
python
import numpy as np作用:NumPy(Numerical Python)是Python科学计算的基础库
- 提供高性能的多维数组对象(ndarray)
- 提供数组运算、线性代数、随机数生成等功能
- 机器学习中用于存储和处理样本数据
2. 数据预处理模块
python
import sklearn.preprocessing as sp作用:sklearn的预处理模块,提供数据预处理功能
sp.scale()- 标准化(均值移除)sp.MinMaxScaler()- 范围缩放sp.normalize()- 归一化sp.Binarizer()- 二值化sp.OneHotEncoder()- 独热编码sp.LabelEncoder()- 标签编码sp.PolynomialFeatures()- 多项式特征扩展
3. 线性模型模块
python
import sklearn.linear_model as lm作用:sklearn的线性模型模块,提供各种回归算法
lm.LinearRegression()- 线性回归lm.Ridge()- 岭回归(L2正则化)lm.Lasso()- Lasso回归(L1正则化)lm.LogisticRegression()- 逻辑回归(分类)
4. 模型评估模块
python
import sklearn.metrics as sm作用:sklearn的评估模块,提供模型性能评价指标
sm.r2_score()- R2决定系数(回归)sm.mean_squared_error()- 均方误差(回归)sm.precision_score()- 查准率(分类)sm.recall_score()- 召回率(分类)sm.f1_score()- F1得分(分类)sm.confusion_matrix()- 混淆矩阵(分类)sm.silhouette_score()- 轮廓系数(聚类)
5. 模型选择模块
python
import sklearn.model_selection as ms作用:sklearn的模型选择模块,提供数据集划分和交叉验证功能
ms.train_test_split()- 划分训练集和测试集ms.cross_val_score()- 交叉验证ms.validation_curve()- 验证曲线ms.learning_curve()- 学习曲线ms.GridSearchCV()- 网格搜索(超参数优化)
6. 支持向量机模块
python
import sklearn.svm as svm作用:sklearn的支持向量机模块
svm.SVC()- 支持向量分类器svm.SVR()- 支持向量回归器
7. 决策树模块
python
import sklearn.tree as st作用:sklearn的决策树模块
st.DecisionTreeRegressor()- 决策树回归器st.DecisionTreeClassifier()- 决策树分类器
8. 朴素贝叶斯模块
python
import sklearn.naive_bayes as nb作用:sklearn的朴素贝叶斯模块
nb.GaussianNB()- 高斯朴素贝叶斯分类器
9. 聚类模块
python
import sklearn.cluster as sc作用:sklearn的聚类模块
sc.KMeans()- K均值聚类sc.DBSCAN()- 噪声密度聚类sc.AgglomerativeClustering()- 凝聚层次聚类
10. 管线模块
python
import sklearn.pipeline as pl作用:sklearn的管线模块,用于串联多个处理步骤
pl.make_pipeline()- 创建处理管线,将预处理和模型串联
11. 集成学习模块
python
import sklearn.ensemble as se作用:sklearn的集成学习模块
se.RandomForestClassifier()- 随机森林分类器se.RandomForestRegressor()- 随机森林回归器
12. 可视化库
python
import matplotlib.pyplot as mp
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d作用:Matplotlib是Python的绘图库
mp.figure()- 创建图形窗口mp.scatter()- 绘制散点图mp.plot()- 绘制折线图mp.show()- 显示图形axes3d- 3D绘图工具
13. 模型持久化
python
import pickle作用:Python的序列化模块
pickle.dump()- 保存模型到文件pickle.load()- 从文件加载模型
第二部分:核心知识点与关键代码
一、回归模型
1. 线性回归(Linear Regression)
名词解释:
- 线性回归 :根据样本数据,寻找一个线性模型
y = wx + b,使得预测值与真实值的误差最小 - 损失函数:度量预测值与真实值差异的函数,常用均方误差(MSE)
- 梯度下降:通过沿着梯度负方向不断调整参数,使损失函数最小化的优化算法
- 学习率(η):梯度下降中参数更新的步长
- R2决定系数:评估回归模型好坏的指标,值越接近1越好
关键代码:
python
# 1. 使用sklearn实现线性回归
import numpy as np
import sklearn.linear_model as lm
import sklearn.metrics as sm
# 准备数据
train_x = np.array([[0.5], [0.6], [0.8], [1.1], [1.4]])
train_y = np.array([5.0, 5.5, 6.0, 6.8, 7.0])
# 创建线性回归器
model = lm.LinearRegression()
# 训练模型
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 预测
pred_y = model.predict(train_x)
# 评估
r2 = sm.r2_score(train_y, pred_y)
print("R2得分:", r2)
print("系数:", model.coef_) # 斜率w
print("截距:", model.intercept_) # 截距b
python
# 2. 多项式回归(处理非线性数据)
import sklearn.pipeline as pl
import sklearn.preprocessing as sp
# 创建多项式回归模型(3次多项式)
model = pl.make_pipeline(
sp.PolynomialFeatures(3), # 多项式特征扩展,最高次项为3
lm.LinearRegression() # 线性回归器
)
# 训练和预测
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = model.predict(train_x)
python
# 3. 岭回归(Ridge)- L2正则化,防止过拟合
model = lm.Ridge(alpha=200, # 正则化强度
max_iter=1000) # 最大迭代次数
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = model.predict(train_x)
python
# 4. Lasso回归 - L1正则化,防止过拟合
model = lm.Lasso(alpha=0.5, # L1范数系数
max_iter=1000) # 最大迭代次数
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = model.predict(train_x)评估指标:
python
# R2决定系数(值越接近1越好,范围[0,1])
r2 = sm.r2_score(y_true, y_pred)
# 均方误差(值越小越好)
mse = sm.mean_squared_error(y_true, y_pred)2. 决策树回归(Decision Tree Regression)
名词解释:
- 决策树:通过树形结构进行决策的模型,每个节点代表一个特征判断
- 叶节点:树的终端节点,存储预测值
- max_depth:树的最大深度,控制模型复杂度
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.tree as st
# 创建决策树回归器
model = st.DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=4) # 最大深度为4
# 训练
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)
# 评估
r2 = sm.r2_score(test_y, pred_y)3. SVM回归(效果较差,不推荐)
python
import sklearn.svm as svm
# 创建SVM回归器
model = svm.SVR(kernel='rbf', # 核函数
C=1.0, # 惩罚参数
gamma='auto') # 核系数
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)二、分类模型
1. 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
名词解释:
- 逻辑回归:虽然名为"回归",但实际是分类算法,通过Sigmoid函数将线性回归结果映射到[0,1]区间
- Sigmoid函数:S型曲线函数,用于二分类概率计算
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.linear_model as lm
# 创建逻辑回归分类器
model = lm.LogisticRegression(
solver='liblinear', # 优化算法
C=1.0 # 正则化强度的倒数
)
# 训练
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)
# 预测概率
pred_proba = model.predict_proba(test_x)2. 决策树分类(Decision Tree Classification)
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.tree as st
# 创建决策树分类器
model = st.DecisionTreeClassifier(
max_depth=4, # 最大深度
criterion='entropy' # 划分标准:'entropy'(信息熵) 或 'gini'(基尼系数)
)
# 训练
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)3. 支持向量机(SVM)
名词解释:
- SVM:寻找最优超平面来划分不同类别的样本
- 核函数:将低维空间映射到高维空间,使线性不可分问题变得可分
- C参数:惩罚参数,控制对误分类的容忍度
- gamma参数:核函数系数,影响决策边界的复杂度
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.svm as svm
# 1. 线性核SVM
model = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1.0)
# 2. 多项式核SVM
model = svm.SVC(kernel='poly',
degree=3, # 多项式次数
C=1.0)
# 3. 径向基核(RBF)SVM - 最常用
model = svm.SVC(kernel='rbf',
C=1.0,
gamma='auto')
# 训练和预测
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)4. 朴素贝叶斯(Naive Bayes)- 只能分类
名词解释:
- 朴素贝叶斯:基于贝叶斯定理和特征独立性假设的分类算法
- 先验概率:事件发生前的概率
- 后验概率:事件发生后的概率
- 高斯朴素贝叶斯:假设特征服从高斯(正态)分布
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.naive_bayes as nb
# 创建高斯朴素贝叶斯分类器
model = nb.GaussianNB()
# 训练
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)三、分类问题评估指标
名词解释:
-
查准率(Precision):预测为正例中真正为正例的比例,评估误检情况
- 公式:
TP / (TP + FP) - 关注:预测的准不准
- 公式:
-
召回率(Recall):真正为正例中被预测为正例的比例,评估漏检情况
- 公式:
TP / (TP + FN) - 关注:找得全不全
- 公式:
-
F1得分:查准率和召回率的调和平均,综合评估
- 公式:
2 * (Precision * Recall) / (Precision + Recall)
- 公式:
-
混淆矩阵:展示分类结果的矩阵,行表示真实类别,列表示预测类别
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.metrics as sm
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
# 1. 划分训练集和测试集
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = ms.train_test_split(
x, y,
test_size=0.25, # 测试集占25%
random_state=7 # 随机种子
)
# 2. 计算查准率
precision = sm.precision_score(
test_y, pred_y,
average='macro' # 多分类:'macro', 'micro', 'weighted'
)
# 3. 计算召回率
recall = sm.recall_score(
test_y, pred_y,
average='macro'
)
# 4. 计算F1得分
f1 = sm.f1_score(
test_y, pred_y,
average='macro'
)
# 5. 混淆矩阵
cm = sm.confusion_matrix(test_y, pred_y)
print("混淆矩阵:\n", cm)
# 6. 准确率(Accuracy)
accuracy = sm.accuracy_score(test_y, pred_y)交叉验证评估:
python
# 交叉验证(5折)
precision_scores = ms.cross_val_score(
model, x, y,
cv=5, # 5折交叉验证
scoring='precision_weighted' # 查准率
)
recall_scores = ms.cross_val_score(
model, x, y,
cv=5,
scoring='recall_weighted' # 召回率
)
f1_scores = ms.cross_val_score(
model, x, y,
cv=5,
scoring='f1_weighted' # F1得分
)
print("查准率:", precision_scores.mean())
print("召回率:", recall_scores.mean())
print("F1得分:", f1_scores.mean())四、聚类模型
名词解释:
- 聚类:无监督学习,将相似的样本划分到同一簇中
- 欧式距离:计算样本间相似度的常用方法
- 簇(Cluster):聚类后的群落
1. K-Means(基于原型聚类)
名词解释:
- K-Means:根据事先给定的聚类数K,随机选择K个中心点,迭代优化
- 聚类中心:每个簇的几何中心
- n_clusters:聚类数量,需要事先指定
特点:
- 优点:简单高效,收敛快
- 缺点:需要事先知道K值,对初始中心敏感,对噪声敏感
- 适用:数据有明显中心,聚类数量已知
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.cluster as sc
import sklearn.metrics as sm
# 创建K-Means聚类器
model = sc.KMeans(n_clusters=4) # 聚类数量为4
# 训练
model.fit(x)
# 获取聚类结果
pred_y = model.labels_ # 每个样本的聚类标签
centers = model.cluster_centers_ # 聚类中心坐标
# 评估:计算轮廓系数
score = sm.silhouette_score(
x, pred_y,
sample_size=len(x),
metric='euclidean' # 欧式距离
)
print("轮廓系数:", score)2. DBSCAN(基于密度聚类)
名词解释:
- DBSCAN:基于密度的聚类算法,不需要事先指定聚类数
- 邻域半径(eps):定义样本邻域的范围
- 最小样本数(min_samples):核心点邻域内的最小样本数
- 核心点:邻域内样本数 >= min_samples的点
- 边界点:可归入某簇但无法扩展新样本的点
- 噪声点:无法归入任何簇的点(标签为-1)
特点:
- 优点:不需要指定K值,能处理噪声,能识别任意形状的簇
- 缺点:对参数敏感,密度不均时效果差
- 适用:数据稠密无明显中心,噪声较多,未知聚类数
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.cluster as sc
# 创建DBSCAN聚类器
model = sc.DBSCAN(
eps=0.8, # 邻域半径
min_samples=5 # 最小样本数
)
# 训练
model.fit(x)
# 获取聚类结果
pred_y = model.labels_ # 聚类标签(-1表示噪声点)
core_indices = model.core_sample_indices_ # 核心样本的索引
# 区分不同类型的点
core_mask = np.zeros(len(x), dtype=bool)
core_mask[core_indices] = True # 核心点
noise_mask = (pred_y == -1) # 噪声点
periphery_mask = ~(core_mask | noise_mask) # 边界点3. 凝聚层次聚类(基于层次)
名词解释:
- 凝聚层次聚类:自底向上,初始每个样本为一簇,逐步合并最近的簇
- linkage :簇间距离计算方式
ward:方差最小化(默认)average:平均距离complete:最大距离
特点:
- 优点:无需初始中心,对中心不明显的数据效果好
- 缺点:需要事先指定聚类数,无法进行预测
- 适用:中心特征不明显的聚类
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.cluster as sc
# 创建凝聚层次聚类器
model = sc.AgglomerativeClustering(
n_clusters=4, # 聚类数量
linkage='ward' # 链接方式
)
# 训练
model.fit(x)
# 获取聚类结果
pred_y = model.labels_五、聚类评估指标
名词解释:
- 轮廓系数(Silhouette Score) :评估聚类质量的指标
- 范围:[-1, 1]
- 值越接近1,聚类效果越好(内密外疏)
- 值接近-1,聚类效果差
- 值接近0,聚类有重叠
关键代码:
python
import sklearn.metrics as sm
# 计算轮廓系数
score = sm.silhouette_score(
x, # 样本数据
pred_y, # 聚类标签
sample_size=len(x), # 样本数量
metric='euclidean' # 距离度量方式
)
print("轮廓系数:", score)六、数据预处理
1. 标准化(均值移除)
名词解释:
- 标准化:使数据均值为0,标准差为1
- 用途:消除量纲影响,提高模型训练效果
python
import sklearn.preprocessing as sp
# 方法1:直接标准化
std_data = sp.scale(raw_data)
# 方法2:创建标准化器
scaler = sp.StandardScaler()
std_data = scaler.fit_transform(raw_data)2. 范围缩放
名词解释:
- 范围缩放:将特征值缩放到指定范围(通常[0,1])
python
# 创建范围缩放器
mms = sp.MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))
scaled_data = mms.fit_transform(raw_data)3. 归一化
名词解释:
- 归一化:每个样本的特征值除以该样本所有特征值的和(或范数)
python
# L1归一化
nor_data = sp.normalize(raw_data, norm='l1')
# L2归一化
nor_data = sp.normalize(raw_data, norm='l2')4. 独热编码
名词解释:
- 独热编码:将分类特征转换为二进制向量,可逆编码
python
# 创建独热编码器
encoder = sp.OneHotEncoder(
sparse=False, # 不使用稀疏矩阵
dtype='int32'
)
# 编码
encoded_data = encoder.fit_transform(raw_data)
# 解码
decoded_data = encoder.inverse_transform(encoded_data)5. 标签编码
名词解释:
- 标签编码:将字符串标签转换为数字标签
python
# 创建标签编码器
encoder = sp.LabelEncoder()
# 编码
encoded_labels = encoder.fit_transform(labels)
# 解码
decoded_labels = encoder.inverse_transform(encoded_labels)七、模型优化
1. 网格搜索(超参数优化)
名词解释:
- 超参数:模型训练前需要设置的参数(如树深度、学习率等)
- 网格搜索:穷举所有参数组合,找到最优参数
python
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
import sklearn.svm as svm
# 定义参数网格
params = [
{'kernel': ['linear'], 'C': [1, 10, 100, 1000]},
{'kernel': ['poly'], 'C': [1], 'degree': [2, 3]},
{'kernel': ['rbf'], 'C': [1, 10, 100], 'gamma': [1, 0.1, 0.01]}
]
# 创建网格搜索对象
model = ms.GridSearchCV(
svm.SVC(), # 基础模型
params, # 参数网格
cv=5 # 5折交叉验证
)
# 训练
model.fit(x, y)
# 获取最优参数和最优得分
print("最优得分:", model.best_score_)
print("最优参数:", model.best_params_)2. 验证曲线
名词解释:
- 验证曲线:评估不同超参数值对模型性能的影响
python
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
# 定义参数范围
param_range = np.arange(50, 550, 50)
# 获取验证曲线
train_scores, test_scores = ms.validation_curve(
model, # 模型
x, y, # 数据
'n_estimators', # 参数名
param_range, # 参数值范围
cv=5 # 交叉验证折数
)
# 计算平均得分
train_mean = train_scores.mean(axis=1)
test_mean = test_scores.mean(axis=1)3. 学习曲线
名词解释:
- 学习曲线:评估不同训练集大小对模型性能的影响
python
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
# 定义训练集大小范围
train_sizes = np.linspace(0.1, 1.0, 10)
# 获取学习曲线
train_sizes, train_scores, test_scores = ms.learning_curve(
model, # 模型
x, y, # 数据
train_sizes=train_sizes, # 训练集大小
cv=5 # 交叉验证
)
train_mean = train_scores.mean(axis=1)
test_mean = test_scores.mean(axis=1)八、模型保存与加载
python
import pickle
# 保存模型
with open('model.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(model, f)
print("模型保存成功")
# 加载模型
with open('model.pkl', 'rb') as f:
model = pickle.load(f)
print("模型加载成功")
# 使用加载的模型预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)第三部分:完整示例代码
示例1:线性回归完整流程
python
import numpy as np
import sklearn.linear_model as lm
import sklearn.metrics as sm
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
import matplotlib.pyplot as mp
# 1. 读取数据
x, y = [], []
with open("data.txt", "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
data = [float(substr) for substr in line.split(",")]
x.append(data[:-1])
y.append(data[-1])
x = np.array(x)
y = np.array(y)
# 2. 划分训练集和测试集
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = ms.train_test_split(
x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=7
)
# 3. 创建并训练模型
model = lm.LinearRegression()
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 4. 预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)
# 5. 评估
r2 = sm.r2_score(test_y, pred_y)
print("R2得分:", r2)
# 6. 可视化
mp.figure('Linear Regression', facecolor='lightgray')
mp.scatter(test_x, test_y, c='blue', label='真实值')
mp.plot(test_x, pred_y, c='red', label='预测值')
mp.legend()
mp.show()示例2:分类问题完整流程
python
import numpy as np
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
import sklearn.metrics as sm
import sklearn.naive_bayes as nb
# 1. 读取数据
x, y = [], []
with open("data.txt", "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
data = [float(substr) for substr in line.split(",")]
x.append(data[:-1])
y.append(data[-1])
x = np.array(x)
y = np.array(y, dtype=int)
# 2. 划分训练集和测试集
train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = ms.train_test_split(
x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=7
)
# 3. 创建并训练模型
model = nb.GaussianNB()
model.fit(train_x, train_y)
# 4. 预测
pred_y = model.predict(test_x)
# 5. 评估
print("查准率:", sm.precision_score(test_y, pred_y, average='macro'))
print("召回率:", sm.recall_score(test_y, pred_y, average='macro'))
print("F1得分:", sm.f1_score(test_y, pred_y, average='macro'))
print("混淆矩阵:\n", sm.confusion_matrix(test_y, pred_y))示例3:聚类问题完整流程
python
import numpy as np
import sklearn.cluster as sc
import sklearn.metrics as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as mp
# 1. 读取数据
x = []
with open("data.txt", "r") as f:
for line in f.readlines():
data = [float(substr) for substr in line.split(",")]
x.append(data)
x = np.array(x)
# 2. 创建并训练K-Means模型
model = sc.KMeans(n_clusters=4)
model.fit(x)
# 3. 获取结果
pred_y = model.labels_
centers = model.cluster_centers_
# 4. 评估
score = sm.silhouette_score(x, pred_y, metric='euclidean')
print("轮廓系数:", score)
# 5. 可视化
mp.figure('K-Means', facecolor='lightgray')
mp.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=pred_y, cmap='brg')
mp.scatter(centers[:, 0], centers[:, 1],
marker='+', c='black', s=200)
mp.show()