在解决哈希冲突问题时,可以使用闭散列和开散列的方式。开散列法又叫做链地址法,首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头节点存储在哈希表中。
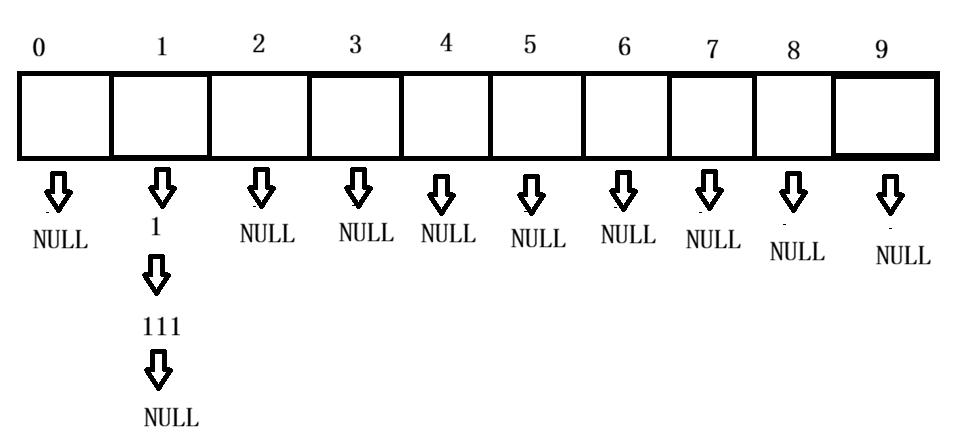
开散列中每一个桶中放的都是发生哈希冲突的元素,这里的哈希桶存储一定数据之后,需要扩容,如果不扩容,不断插入后哈希桶会越来越长,效率得不到保障(负载因子控制在1,平均一个哈希桶一个数据)。
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
namespace hash_bucket
{
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_kv(kv)
,_next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K, class V>
class HashTable
{
public:
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(10, nullptr);
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
// 负载因子到1就扩容
if (_n == _table.size())
{
size_t newSize = _table.size() * 2;
vector<Node*> newTable;
newTable.resize(newSize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = cur->_kv.first % newSize;
cur->_next = newTable[hashi];
newTable[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.swap(newTable);
}
size_t hashi = kv.first % _table.size();
// 头插
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
newnode->_next = _table[hashi];
_table[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
void Print()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i)
{
printf("[%d]->", i);
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
cout << cur->_kv.first << "->";
cur = cur->_next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _table.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
// delete
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_table[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
~HashTable()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}