
💡Yupureki:个人主页
🌸Yupureki🌸的简介:
目录
[1. 马的遍历](#1. 马的遍历)
[2. kotori和迷宫](#2. kotori和迷宫)
[3. Catch That Cow S](#3. Catch That Cow S)
[4. 八数码难题](#4. 八数码难题)
前言
BFS,又称宽度优先搜索。和DFS不一样的是,BFS不是一条路走到死,而是由一个起点开始一层一层地搜索,跟二叉树的层序遍历基本一致。因此BFS可以找出距离起始状态的最近的某个特定状态。
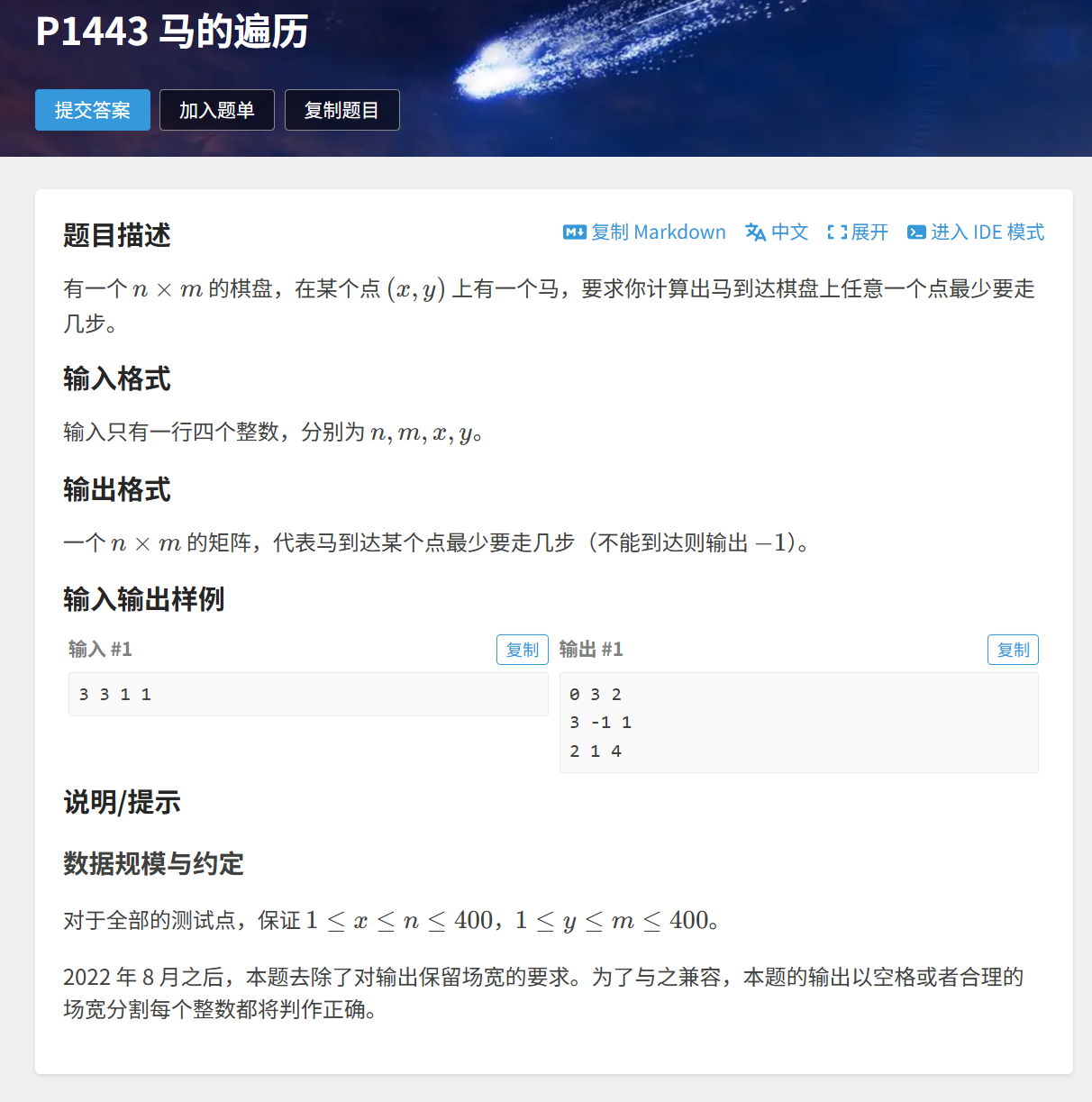
1. 马的遍历
题目链接:
算法原理
题目要求到达某个点最少要走几步,因此可以用bfs解决。因为当权值为1时,bfs每次都是扩展距离起点等距离的一层,天然具有最短性。那就从起点开始,一层一层的往外搜,用一个数组记录最短距离。同时我们还需要用dx和dy两个偏移量来实现马的走法
关于bfs实现,参考二叉树的层序遍历,用一个queue队列来记录每一层的节点。
实操代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
int x, y;
int dx[8] = { 1,2,2,1,-1,-2,-2,-1 };
int dy[8] = { 2,1,-1,-2,2,1,-1,-2 };
void bfs()
{
vector<vector<int>> v(n, vector<int>(m, -1));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ x,y });
v[x][y] = 0;
while (q.size())
{
auto p = q.front();
int a = p.first;
int b = p.second;
q.pop();
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int i = a + dx[k];
int j = b + dy[k];
if (i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m || v[i][j] != -1)
continue;
q.push({ i,j });
v[i][j] = v[a][b] + 1;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < v[0].size(); j++)
{
cout << v[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m>>x>>y;
x--; y--;
bfs();
return 0;
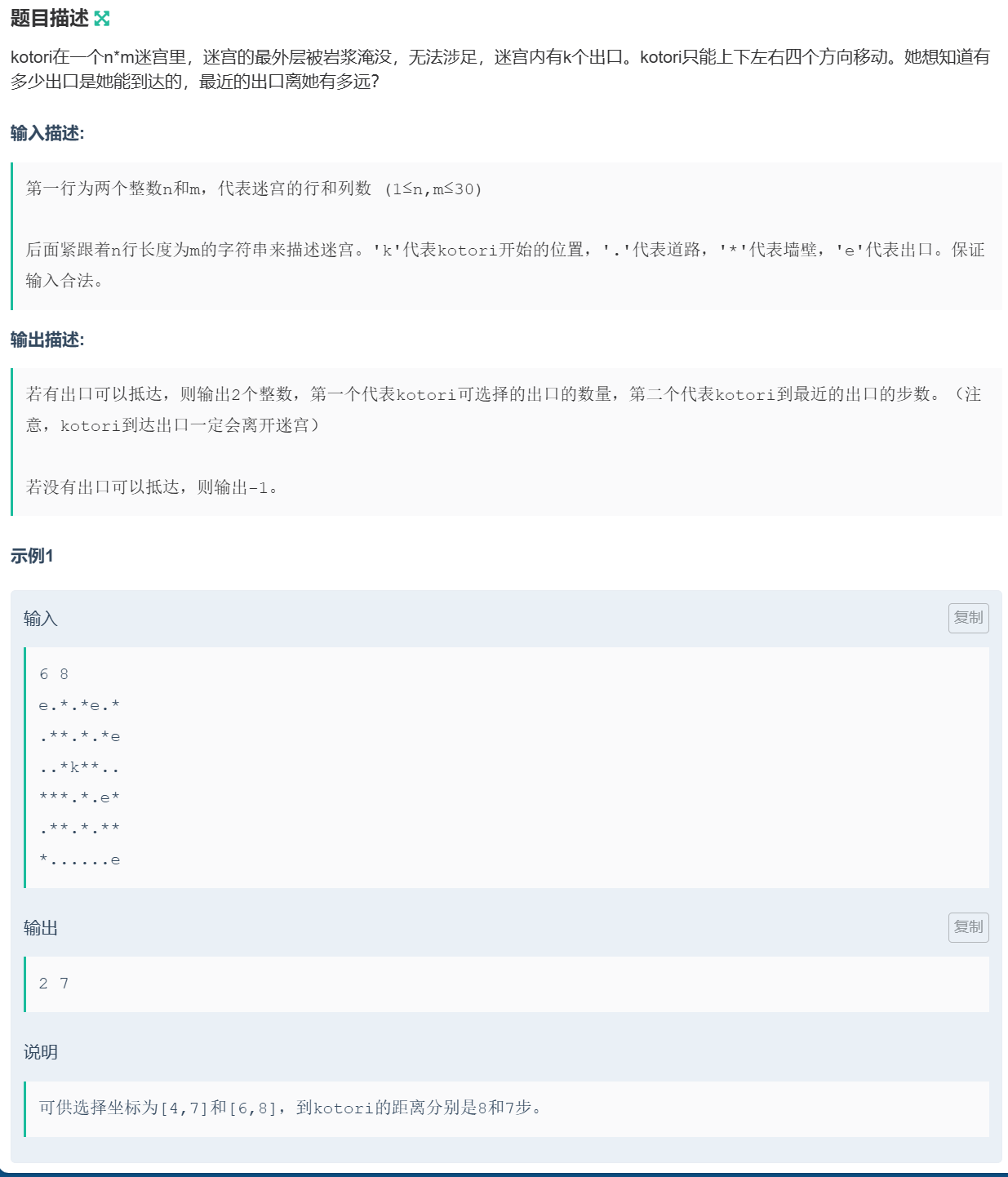
}2. kotori和迷宫
题目链接:
算法原理
经典 bfs问题。
从迷宫的起点位置逐层开始搜索,每搜到一个点就标记一下最短距离。当把整个迷宫全部搜索完毕之后,扫描整个标记数组,求出出口的数量以及最短的距离。关于走法,之前有讲,用dx和dy两个偏移量模拟人的走法
如果遇到了墙壁或者演讲,直接continue掉即可
实操代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int x, y;
vector<vector<char>> v;
vector<vector<bool>> visited; // 使用单独的访问标记数组
int ret = 0xffffff;
int num = 0;
int n, m;
int dx[4] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
void bfs() {
vector<vector<int>> dist(n, vector<int>(m, -1));
visited.resize(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({x, y});
dist[x][y] = 0;
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
int a = p.first;
int b = p.second;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int i = a + dx[k];
int j = b + dy[k];
if (i < 0 || i >= n || j < 0 || j >= m)
continue;
if (visited[i][j] || v[i][j] == '*')
continue;
dist[i][j] = dist[a][b] + 1;
visited[i][j] = true;
if (v[i][j] == 'e') {
ret = min(ret, dist[i][j]);
num++;
} else {
q.push({i, j});
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
v.resize(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
v[i].resize(m);
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> v[i][j];
if (v[i][j] == 'k') {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
bfs();
if (num == 0) {
cout << -1 << endl;
} else {
cout << num << " " << ret << endl;
}
return 0;
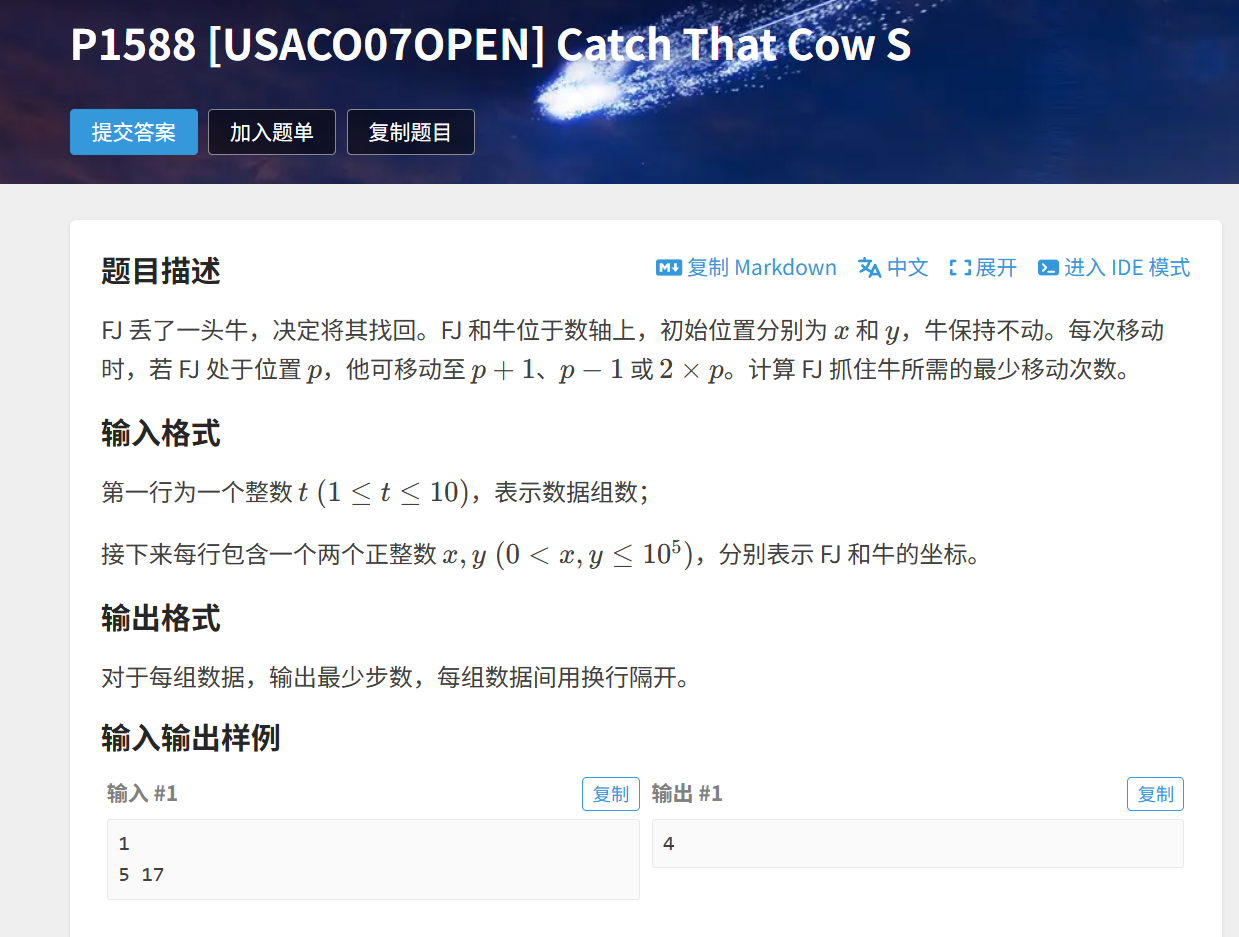
}3. Catch That Cow S
题目链接:
算法原理
可以暴力枚举出所有的行走路径,因为是求最少步数,所以可以用bfs解决:
- 从起点位置开始搜索,每次向外扩展三种行走方式;
- 当第一次搜到牛的位置时,就是最短距离。
如果不做任何处理,时间和空间都会超。因为我们会搜索到很多无效的位置,所以我们要加上剪枝策略:
- 当-1减到负数的时候,剪掉;因为如果走到负数位置,还是需要回头走到正数位置,一定不是最优解。
- 当+1操作越过y的时候,剪掉。如果+1之后大于y,说明本身就在y位置或者y的右侧,你再往右走还是需要再向左走回去。一定不是最优解,剪掉。
- 当y是偶数,并且当*2操作之后大于y的时候,剪掉,因为不如先减到y的一半然后再乘;设当前数是x,那么:先乘后减,总的步数t=2x-y+1;先减后乘,总的步数t2=x-y/2+1;ti-t2 = x-y/2>0;因此,先乘后减不如先减后乘。
- 设y是奇数的时候,那么y+1就是偶数,根据3可得,*2操作不能超过y+1。
实操代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n = 1e5;
int x, y;
int dist[N];
void bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
dist[x] = 0;
while (q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int a = t + 1, b = t - 1, c = t * 2;
if (a <= n && dist[a] == -1)
{
dist[a] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(a);
}
if (b > 0 && dist[b] == -1)
{
dist[b] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(b);
}
if (c <= n && dist[c] == -1)
{
dist[c] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(c);
}
if (a == y || b == y || c == y) return;
}
}
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T;
while (T--)
{
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
cin >> x >> y;
bfs();
cout << dist[y] << endl;
}
return 0;
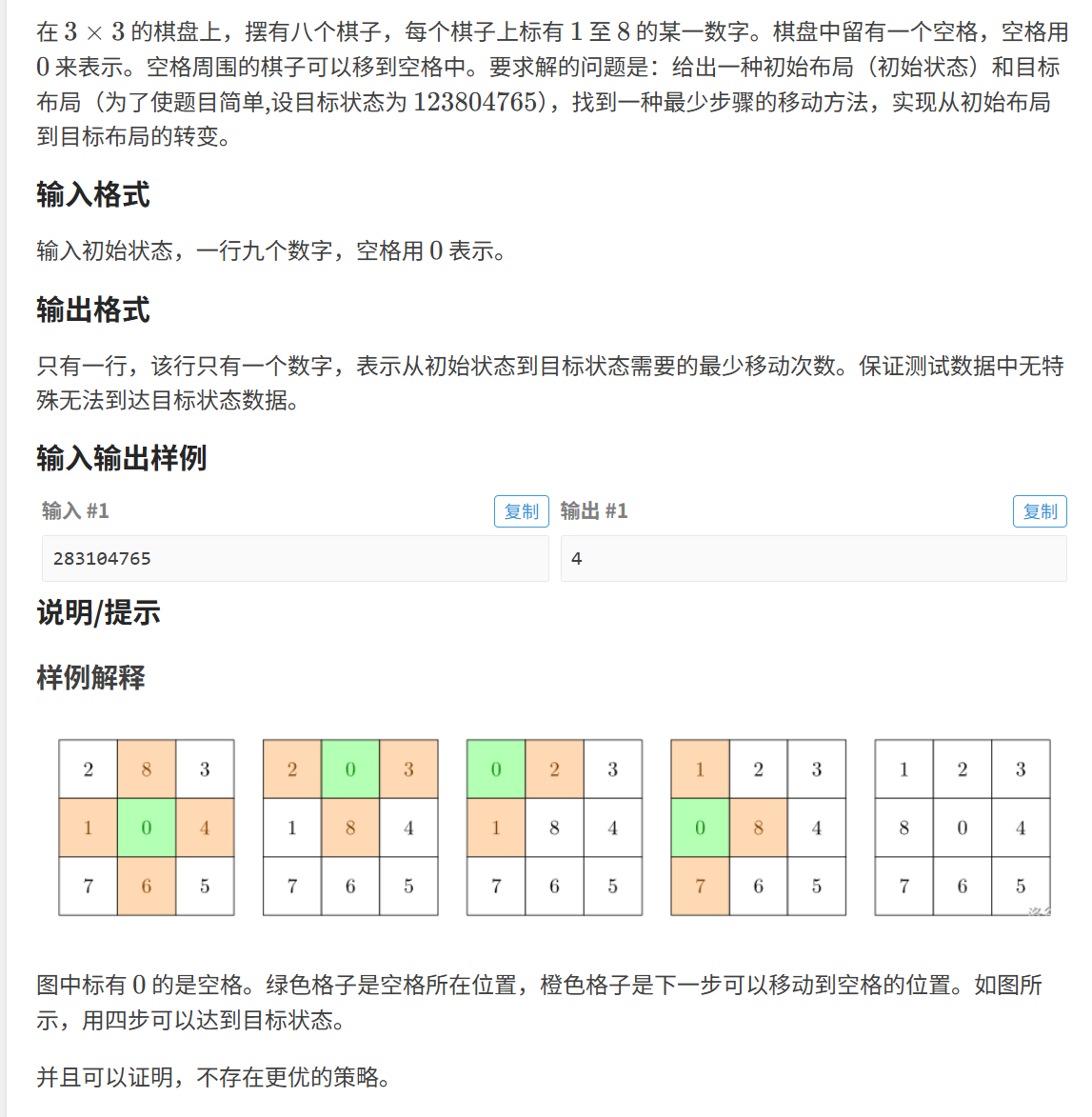
}4. 八数码难题
题目链接:
算法原理
经过之前那么多题的铺垫,这道题的解法还是容易想到的。因为要求的是最短步数,因此可以用bfs解决。
- 从起始状态开始,每次扩展上下左右交换后的状态;
- 在搜索的过程中,第一次遇到最终状态就返回最短步数。
即我们无脑用bfs枚举0的所有走法,直到达到目标状态
期间我们肯定会遇到重复的状态,即之前已经达到了。例如0往上移动了,又往下移动,那就跟没走一样。因此我们用unordered_map<string,int> 记录达到该状态的最短步数,如果已经存在了就直接返回
关于记录的状态类型,我选择用string记录,即棋盘从左到右,从上到下的数字串在一起用字符串表示,就跟题目给出的初始状态一样
如何通过一个字符串找到交换之后的字符串?
策略一:先把字符串还原成二维矩阵,然后交换0与四周的数字,最后再把交换之后的棋盘还原
成字符串。
虽然可行,但是太过于麻烦。我们其实可以通过计算,快速得出二维坐标与一维下标相互转换前后
的值。如下图:
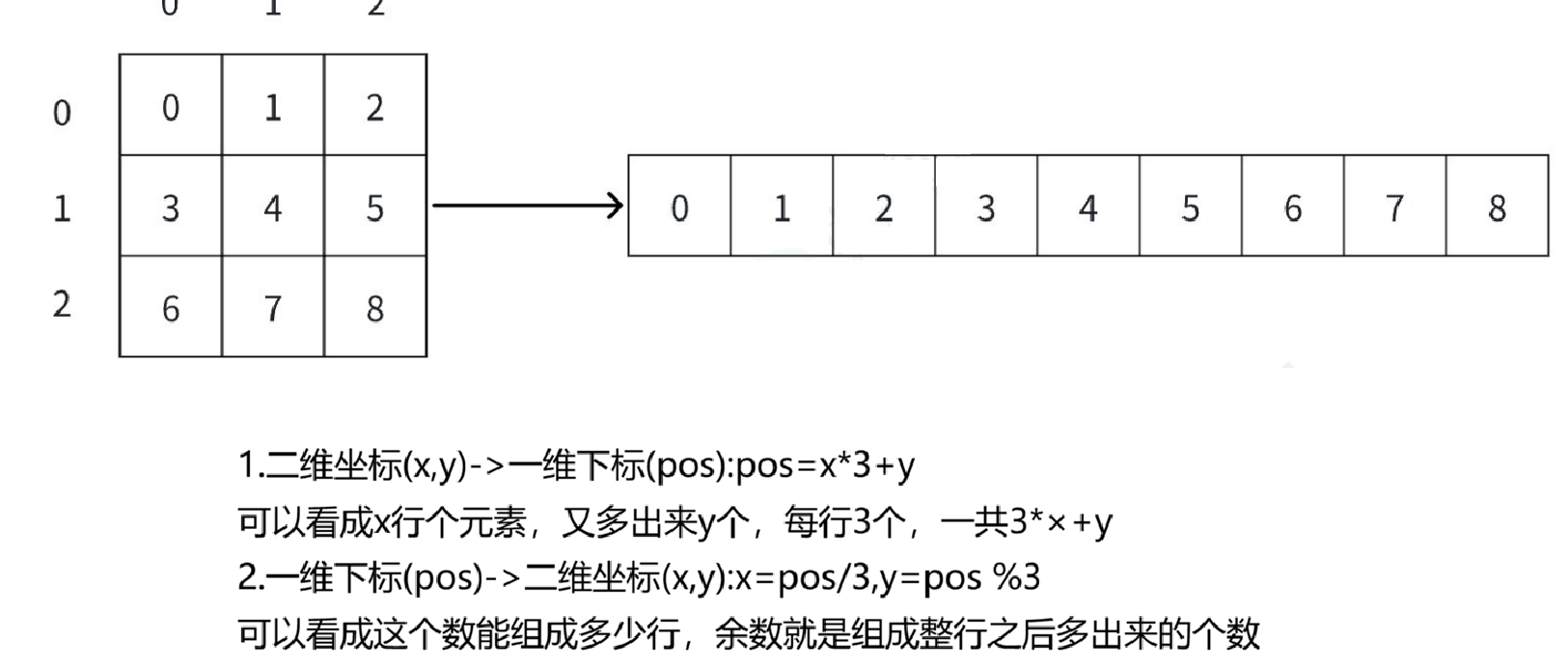
我们每次找到字符串中0的下标pos,这样就能转换成二维坐标,然后再用二维坐标上下左右移动
实操代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
string start;
unordered_map<string, int> mem;//记录每个状态的最短步数
int dx[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
int dy[4] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
void dfs()
{
if(start == "123804765")
{
cout<<0;
return;
}
queue<string> q;
mem.insert({ start,0 });
q.push(start);
while (q.size())
{
string s = q.front();
q.pop();
int pos = 0;
for (auto& it : s)//找到字符串0的下标
{
if (it == '0')
break;
pos++;
}
int a = pos / 3;//一维坐标转二维坐标
int b = pos % 3;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = a + dx[k];
int y = b + dy[k];
if (x < 0 || x > 2 || y < 0 || y > 2)
continue;
string next = s;
int pos2 = x * 3 + y;//二维坐标转一维坐标
swap(next[pos2], next[pos]);//交换元素
if (mem.find(next) != mem.end())
continue;
mem[next] = mem[s] + 1;
q.push(next);
if (next == "123804765")
{
cout << mem[next];
return;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> start;
dfs();
return 0;
}