前言
- 这个专栏将会用纯C实现常用的数据结构和简单的算法;
- 有C基础即可跟着学习,代码均可运行;
- 准备考研的也可跟着写,个人感觉,如果时间充裕,手写一遍比看书、刷题管用很多,这也是本人采用纯C语言实现的原因之一;
- 欢迎收藏 + 关注,本人将会持续更新。
文章目录
什么是哈希
📘 概念:哈希结构(Hash Table)也被称为散列表,是一种用于实现字典(Dictionary)的数据结构。
重点 :散列表,这个刷过算法的人应该都知道这个数据结果,散列表 的特点就是查找特别快,典型应用 :判断A集合是否存在B集合;字典结构,我感觉学过Python或者JS都很清楚这个特点了;
🔴 重点概念
- 哈希结构 通过键
Key映射到值Value的过程称为哈希 ,映射学过数学应该都知道这个概念,函数就是典型的映射关系; - 哈希函数:将键 映射到一个存储位置的函数;
⏫ 用处
哈希用处很多,最核心 的应用是查找 ,哈希查找速度很快,如:用数组作为哈希结构容器,假设我们要存储一段数据(1, 5, 100, 10000, 100000),想要查找最快,找到数组下标即可 ,但是这个最大值很大(100000),如果申请这么大的内存,储存量却很少,这就造成了内存浪费,但是用哈希结构的一些方法,可以很大的节省时间 ,数组也是一种哈希结构,这个后面我们会讲。
哈希构造函数
🏡 概念 哈希构造函数(Hash Constructor)是哈希结构中的一种函数,用于将键(Key)映射到哈希表中的位置。哈希构造函数通常是一个确定性函数,即对于相同的键,哈希构造函数总是返回相同的哈希值。哈希构造函数的设计非常关键,它直接影响哈希结构的查找、插入和删除等操作的效率。
重点:
- 哈希函数:将键值映射到哈希表中位置;
- 哈希构造函数通常是一个确定性函数,即对于相同的键,哈希构造函数总是返回相同的哈希值,键与射的值相互对于,具有唯一性;
- 哈希构造函数的设计非常关键,但是这个一般我感觉需要结合业务场景,根据不同数据从而选取不同的哈希函数,下面会有一些常用的哈希函数。
🌓 哈希构造函数的设计需要满足以下几个要求:
- 一致性:对于相同的键,哈希构造函数应该总是返回相同的哈希值。
- 均匀性:哈希构造函数应该尽可能均匀地将键映射到哈希表中的位置,以避免哈希冲突。
- 高效性:哈希构造函数的计算时间应该尽可能短,以提高哈希结构的操作效率。
🌌 哈希构造函数的设计方法有很多种,常见的方法包括:
-
直接寻址法(Direct Addressing):将键直接作为哈希表中的位置,适用于键的范围比较小的情况。
-
除留余数法(Division Method):将键除以一个不大于哈希表大小的质数 ,然后取余数作为哈希值,h*(*k)= k mod m,m 是哈希表的大小,即输出哈希值的范围,这个也是最常用的,一般来说,m不能过于靠近2的幂。
-
乘法哈希法(Multiplicative Hashing):将键乘以一个常数A(0<A<1),然后取乘积的小数部分乘以哈希表大小作为哈希值。

-
一次探测法(Linear Probing):当发生哈希冲突时,依次向后探测空桶,直到找到空桶或者遍历整个哈希表。
-
双重哈希法(Double Hashing):使用两个不同的哈希函数,当发生哈希冲突时,依次使用两个哈希函数计算出新的哈希值,直到找到空桶或者遍历整个哈希表。
🌾 当然还有其他,注意 :像除留余数法,为什么需要除以不大于哈希表最大大小的质数,这是是有严格的数学证明,可以减少哈希冲突概率,记住即可。
哈希解决冲突方法
这个有很多,如:开放地址寻址法、再次哈希法、链地址法、建立公共溢出区,这里只讲解,开放地址寻址法和链地址法。
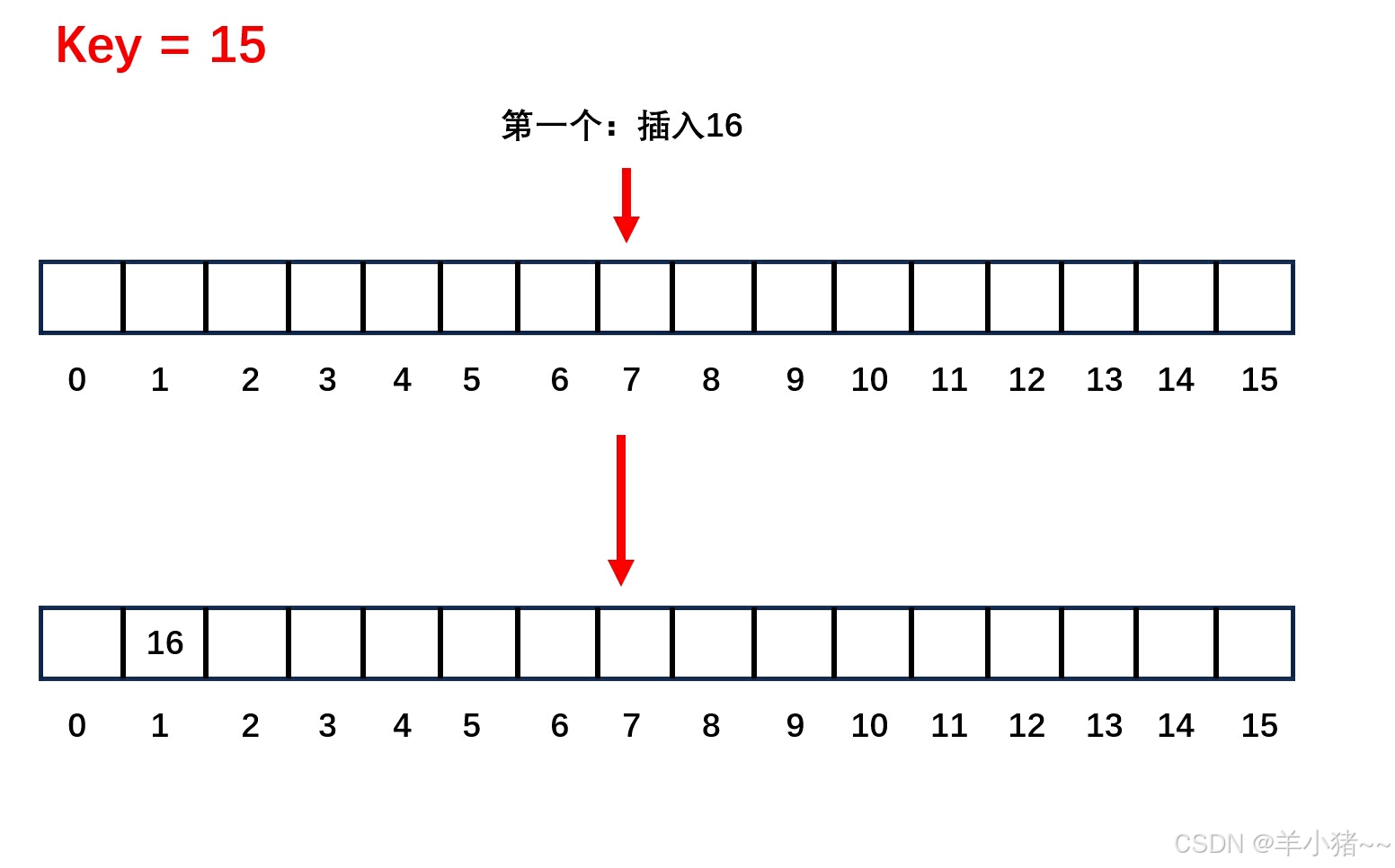
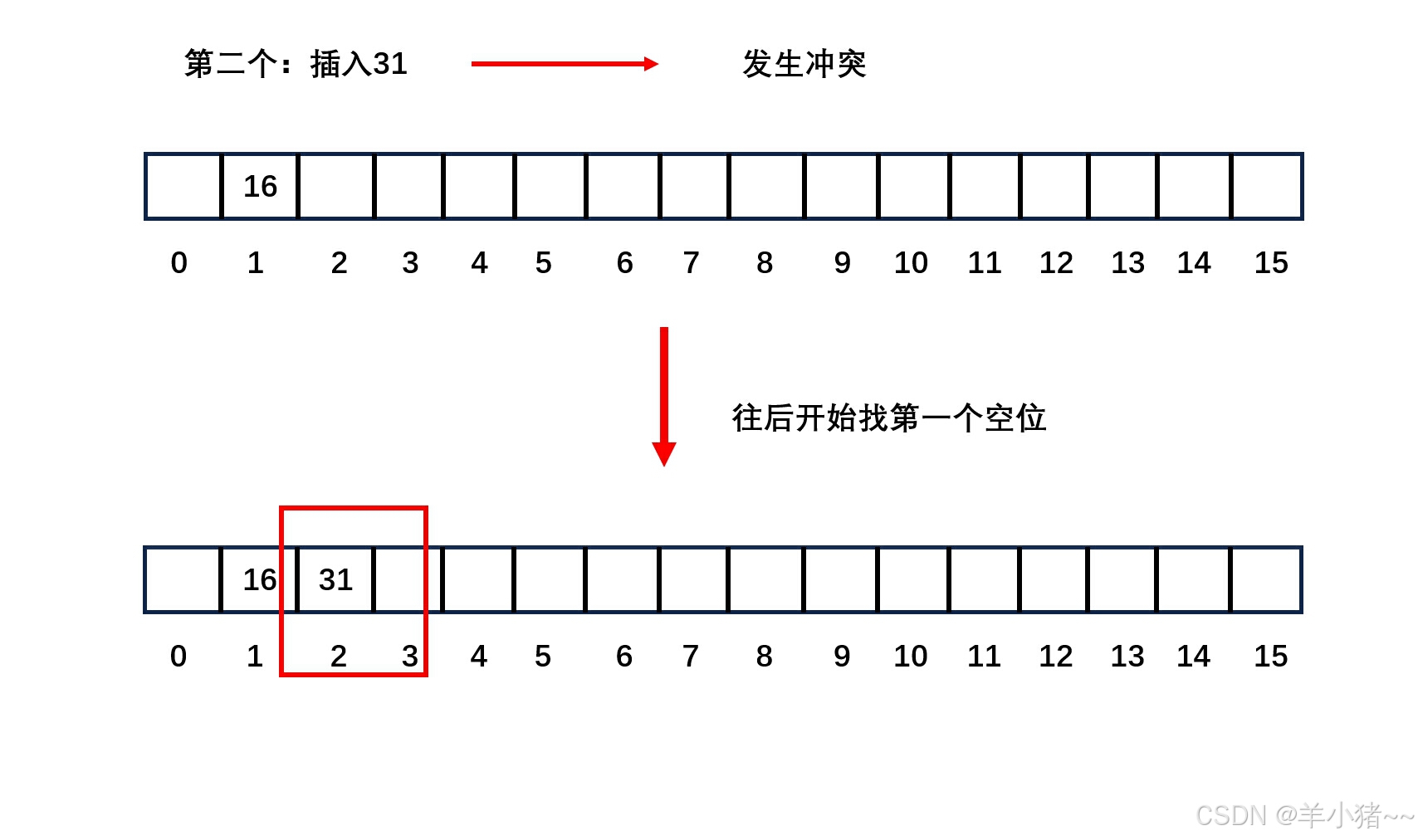
开放地址寻址法
开发地址寻址法就是在发生哈希冲突的时候,在哈希映射那个点往后寻找,寻找到一个空位即可。
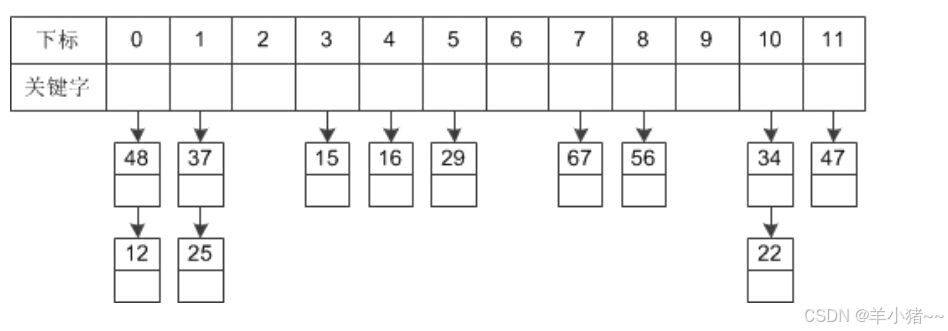
链地址法
链地址法就是用一个链表,当发生哈希冲突的时候,在哈希映射那个位置,拉一条链表,将数据填入链表中。
数组哈希案例实现
封装
cpp
// 这里假设存储的数据是这个,key是自己抽象出来的
typedef struct Data {
int key;
char buffer[20];
}Data;
typedef struct Hash {
Data** data;
int p;
int count;
}Hash;创建哈希
cpp
Hash* create_hash(int p)
{
Hash* hash = (Hash*)calloc(1, sizeof(Hash));
assert(hash);
hash->data = (Data**)calloc(p, sizeof(Data));
assert(hash->data);
hash->p = p;
return hash;
}得到哈希映射值
cpp
// 如果相同key值,则覆盖
int get_index(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
int pos = data.key % hash->p;
int curPos = pos;
do {
if (hash->data[curPos] == NULL || hash->data[curPos]->key == data.key) {
return curPos;
}
curPos = (curPos + 1) % hash->p;
} while (curPos != pos);
return -1; // 找不到,则当前满了,这里假设数据能够存储
}插入数据
cpp
void push(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
int pos = get_index(hash, data);
if (pos == -1) {
return;
}
if (hash->data[pos] == NULL) {
Data* newData = (Data*)calloc(1, sizeof(Data));
assert(newData);
hash->data[pos] = newData;
// 内存拷贝
memcpy(hash->data[pos], &data, sizeof(data));
}
else {
if (hash->data[pos]->key == data.key) {
// 字符串拷贝
strcpy(hash->data[pos]->buffer, data.buffer);
}
}
hash->count++;
}哈希查找
循环查找一圈看是否能找到。
cpp
Data* search(Hash* hash, int key)
{
assert(hash);
int pos = key % hash->count;
int curPos = pos;
do {
if (hash->data[curPos] == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (hash->data[curPos]->key == key) {
return hash->data[curPos];
}
curPos = (curPos + 1) % hash->p;
} while (pos != curPos);
return NULL;
}总代码
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
f(key) = key / p;
*/
// 这里假设存储的数据是这个,key是自己抽象出来的
typedef struct Data {
int key;
char buffer[20];
}Data;
typedef struct Hash {
Data** data;
int p;
int count;
}Hash;
Hash* create_hash(int p)
{
Hash* hash = (Hash*)calloc(1, sizeof(Hash));
assert(hash);
hash->data = (Data**)calloc(p, sizeof(Data));
assert(hash->data);
hash->p = p;
return hash;
}
// 如果相同key值,则覆盖
int get_index(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
int pos = data.key % hash->p;
int curPos = pos;
do {
if (hash->data[curPos] == NULL || hash->data[curPos]->key == data.key) {
return curPos;
}
curPos = (curPos + 1) % hash->p;
} while (curPos != pos);
return -1; // 找不到,则当前满了,这里假设数据能够存储
}
void push(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
int pos = get_index(hash, data);
if (pos == -1) {
return;
}
if (hash->data[pos] == NULL) {
Data* newData = (Data*)calloc(1, sizeof(Data));
assert(newData);
hash->data[pos] = newData;
// 内存拷贝
memcpy(hash->data[pos], &data, sizeof(data));
}
else {
if (hash->data[pos]->key == data.key) {
// 字符串拷贝
strcpy(hash->data[pos]->buffer, data.buffer);
}
}
hash->count++;
}
void print_hash(Hash* hash)
{
assert(hash);
for (int i = 0; i < hash->p; i++) {
if (hash->data[i] == NULL) {
printf("NULL\n");
}
else {
printf("%d %s\n", hash->data[i]->key, hash->data[i]->buffer);
}
}
}
Data* search(Hash* hash, int key)
{
assert(hash);
int pos = key % hash->count;
int curPos = pos;
do {
if (hash->data[curPos] == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (hash->data[curPos]->key == key) {
return hash->data[curPos];
}
curPos = (curPos + 1) % hash->p;
} while (pos != curPos);
return NULL;
}
int size(Hash* hash)
{
assert(hash);
return hash->count;
}
bool empty(Hash* hash)
{
assert(hash);
return hash->count == 0;
}
int main()
{
Hash* hash = create_hash(11);
Data data[8] = { 1,"小美",11,"小芳",25,"花花",38,"coco",45,"小帅",88,"baby",65,"小丽",75,"小小" };
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
push(hash, data[i]);
}
print_hash(hash);
Data* sdata = search(hash, 45);
printf("search: %d %s\n", sdata->key, sdata->buffer);
return 0;
}链表哈希案例实现
封装
cpp
// 数据封装
typedef struct Data {
int key;
char buffer[20];
}Data;
// 横向链表节点封装(解决冲突节点)
typedef struct LNode {
Data data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode;
// 纵向链表节点封装
typedef struct SNode {
Data data;
struct SNode* snext;
LNode* lnext; // 解决冲突链表
}SNode;
// 哈希封装
typedef struct Hash {
SNode* headNode;
int p; // 余数
int count; // 存储的元素个数
}Hash;
LNode* create_lnode(Data data)
{
LNode* node = (LNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(LNode));
assert(node);
node->data = data;
return node;
}
SNode* create_snode(Data data)
{
SNode* node = (SNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(SNode));
assert(node);
node->data = data;
return node;
}
Hash* create_hash(int p)
{
Hash* hash = (Hash*)calloc(1, sizeof(Hash));
assert(hash);
hash->p = p;
return hash;
}插入
这个确实规矩有点多,如:
- 第一步得到哈希映射值
- 如果在主链表中已经存在了,则在主链表映射位置拉一条链表,头插(这里是)
- 如果主链表中不存在,则插入主链表中
cpp
// 插入
// 规则有点多
void push(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
// 创建节点
SNode* new_node = create_snode(data);
int pos = data.key % hash->p;
// 没有,则纵向链表生成
if (hash->headNode == NULL) {
hash->headNode = new_node;
}
else { // 检查
SNode* insert = hash->headNode;
SNode* prevInsert = NULL;
//
if (insert->data.key % hash->p > pos) {
new_node->snext = hash->headNode;
hash->headNode = new_node;
hash->count++;
}
else {
while (insert != NULL && (insert->data.key % hash->p < pos)) {
prevInsert = insert;
insert = insert->snext;
}
//
if (insert == NULL) {
prevInsert->snext = new_node;
hash->count++;
}
else if (insert->data.key % hash->p == pos) {
//
if (insert->data.key == data.key) {
strcpy(insert->data.buffer, data.buffer);
}
else {
LNode* curNode = insert->lnext;
if (curNode == NULL) {
insert->lnext = create_lnode(data);
hash->count++;
}
else {
// 横向插入,头插
while (curNode != NULL && curNode->data.key != data.key) {
curNode = curNode->next;
}
// 没有,头插
if (curNode == NULL) {
LNode* temp = create_lnode(data);
temp->next = insert->lnext;
insert->lnext = temp;
hash->count++;
}
else { // 有,覆盖
strcpy(curNode->data.buffer, data.buffer);
}
}
}
}
else {
new_node->snext = insert;
prevInsert->snext = new_node;
hash->count++;
}
}
}
}查找
这个查找分为两个步骤:
- 主链表中找(纵向)
- 在映射值的那个链表中找
cpp
// 打印
void print_hash(Hash* hash)
{
assert(hash);
SNode* rTemp = hash->headNode;
while (rTemp) {
printf("key: %d, value: %s", rTemp->data.key, rTemp->data.buffer);
if (rTemp->lnext != NULL) {
printf(" 【");
LNode* lTemp = rTemp->lnext;
while (lTemp != NULL) {
printf("key: %d, value: %s", lTemp->data.key, lTemp->data.buffer);
lTemp = lTemp->next;
}
printf(" 】");// 看清楚这个是行的数据
}
rTemp = rTemp->snext;
printf("\n");
}
}
// 查找
enum MatchType
{
NoMatch, // 没有
RowMatch, // 纵找到
ColMatch // 横找到
};
typedef struct Match {
int type;
union {
LNode* lnode;
SNode* snode;
};
}Match;
Match search(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
Match res = { 0 };
int pos = data.key % hash->p;
SNode* rTemp = hash->headNode;
while (rTemp) {
if (pos == rTemp->data.key % hash->p) {
if (data.key == rTemp->data.key) {
res.type = RowMatch;
res.snode = rTemp;
return res;
}
else {
LNode* lTemp = rTemp->lnext;
while (lTemp) {
if (lTemp->data.key == data.key) {
res.type = ColMatch;
res.lnode = lTemp;
return res;
}
lTemp == lTemp->next;
}
}
}
rTemp = rTemp->snext;
}
return res;
}
void print_search(Match match)
{
switch (match.type)
{
case NoMatch:
printf("没有找到\n");
break;
case RowMatch:
printf("找到了,key: %d, value: %s\n", match.snode->data.key, match.snode->data.buffer);
break;
case ColMatch:
printf("找到了,key: %d, value: %s\n", match.lnode->data.key, match.lnode->data.buffer);
break;
}
}总代码
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
// 链表实现哈希,使用链表法解决冲突,要注意的是封装会比较多
// 假设不处理重复值
// 数据封装
typedef struct Data {
int key;
char buffer[20];
}Data;
// 横向链表节点封装(解决冲突节点)
typedef struct LNode {
Data data;
struct LNode* next;
}LNode;
// 纵向链表节点封装
typedef struct SNode {
Data data;
struct SNode* snext;
LNode* lnext; // 解决冲突链表
}SNode;
// 哈希封装
typedef struct Hash {
SNode* headNode;
int p; // 余数
int count; // 存储的元素个数
}Hash;
LNode* create_lnode(Data data)
{
LNode* node = (LNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(LNode));
assert(node);
node->data = data;
return node;
}
SNode* create_snode(Data data)
{
SNode* node = (SNode*)calloc(1, sizeof(SNode));
assert(node);
node->data = data;
return node;
}
Hash* create_hash(int p)
{
Hash* hash = (Hash*)calloc(1, sizeof(Hash));
assert(hash);
hash->p = p;
return hash;
}
// 插入
// 规则有点多
void push(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
// 创建节点
SNode* new_node = create_snode(data);
int pos = data.key % hash->p;
// 没有,则纵向链表生成
if (hash->headNode == NULL) {
hash->headNode = new_node;
}
else { // 检查
SNode* insert = hash->headNode;
SNode* prevInsert = NULL;
//
if (insert->data.key % hash->p > pos) {
new_node->snext = hash->headNode;
hash->headNode = new_node;
hash->count++;
}
else {
while (insert != NULL && (insert->data.key % hash->p < pos)) {
prevInsert = insert;
insert = insert->snext;
}
//
if (insert == NULL) {
prevInsert->snext = new_node;
hash->count++;
}
else if (insert->data.key % hash->p == pos) {
//
if (insert->data.key == data.key) {
strcpy(insert->data.buffer, data.buffer);
}
else {
LNode* curNode = insert->lnext;
if (curNode == NULL) {
insert->lnext = create_lnode(data);
hash->count++;
}
else {
// 横向插入,头插
while (curNode != NULL && curNode->data.key != data.key) {
curNode = curNode->next;
}
// 没有,头插
if (curNode == NULL) {
LNode* temp = create_lnode(data);
temp->next = insert->lnext;
insert->lnext = temp;
hash->count++;
}
else { // 有,覆盖
strcpy(curNode->data.buffer, data.buffer);
}
}
}
}
else {
new_node->snext = insert;
prevInsert->snext = new_node;
hash->count++;
}
}
}
}
// 打印
void print_hash(Hash* hash)
{
assert(hash);
SNode* rTemp = hash->headNode;
while (rTemp) {
printf("key: %d, value: %s", rTemp->data.key, rTemp->data.buffer);
if (rTemp->lnext != NULL) {
printf(" 【");
LNode* lTemp = rTemp->lnext;
while (lTemp != NULL) {
printf("key: %d, value: %s", lTemp->data.key, lTemp->data.buffer);
lTemp = lTemp->next;
}
printf(" 】");// 看清楚这个是行的数据
}
rTemp = rTemp->snext;
printf("\n");
}
}
// 查找
enum MatchType
{
NoMatch, // 没有
RowMatch, // 纵找到
ColMatch // 横找到
};
typedef struct Match {
int type;
union {
LNode* lnode;
SNode* snode;
};
}Match;
Match search(Hash* hash, Data data)
{
assert(hash);
Match res = { 0 };
int pos = data.key % hash->p;
SNode* rTemp = hash->headNode;
while (rTemp) {
if (pos == rTemp->data.key % hash->p) {
if (data.key == rTemp->data.key) {
res.type = RowMatch;
res.snode = rTemp;
return res;
}
else {
LNode* lTemp = rTemp->lnext;
while (lTemp) {
if (lTemp->data.key == data.key) {
res.type = ColMatch;
res.lnode = lTemp;
return res;
}
lTemp == lTemp->next;
}
}
}
rTemp = rTemp->snext;
}
return res;
}
void print_search(Match match)
{
switch (match.type)
{
case NoMatch:
printf("没有找到\n");
break;
case RowMatch:
printf("找到了,key: %d, value: %s\n", match.snode->data.key, match.snode->data.buffer);
break;
case ColMatch:
printf("找到了,key: %d, value: %s\n", match.lnode->data.key, match.lnode->data.buffer);
break;
}
}
int main()
{
Hash* hash = create_hash(11);
Data data[8] = { 1,"小美",11,"小芳",25,"花花",38,"coco",42,"小帅",88,"baby",66,"小丽",77,"小小" };
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
push(hash, data[i]);
}
print_hash(hash);
printf("********************\n");
Match search_res = search(hash, data[3]);
print_search(search_res);
return 0;
}